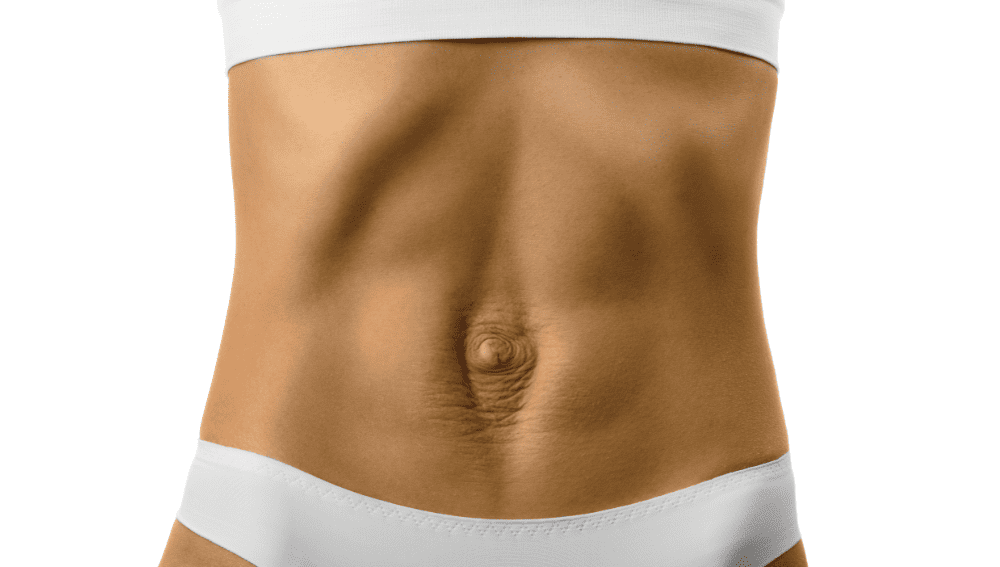
Diastasis recti is a common condition that affects many people, especially women during and after pregnancy. It occurs when the rectus abdominis muscles in the abdomen separate, causing a bulge or protrusion in the midline of the abdomen.
While diastasis recti is usually not a serious medical condition, it can cause a range of symptoms, including back pain, poor posture, and weakened pelvic floor muscles.
Recent studies have suggested that diastasis recti may also be linked to bowel problems, such as constipation and bloating. This is because the separation of the abdominal muscles can weaken the abdominal wall, making it harder to push waste through the digestive system.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between diastasis recti and bowel problems, it is important for people with this condition to be aware of the potential risks and seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
Key Takeaways
- Diastasis recti is a common condition that can cause a range of symptoms, including back pain, poor posture, and weakened pelvic floor muscles.
- Recent studies have suggested that diastasis recti may be linked to bowel problems, such as constipation and bloating.
- While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between diastasis recti and bowel problems, it is important for people with this condition to be aware of the potential risks and seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
Understanding Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is a condition that affects the abdominal muscles. It occurs when the rectus abdominis muscles, which run vertically down the abdomen, separate from each other.
This separation causes a gap between the muscles, which can weaken the abdominal wall and lead to a bulge in the stomach.
The rectus abdominis muscles are important for supporting the core and maintaining good posture. They play a crucial role in activities such as lifting, bending, and twisting.
The muscles are connected by a band of tissue called the linea alba, which can also become stretched or weakened in diastasis recti.
Diastasis recti can occur in anyone, but it is most commonly seen in pregnant women and those who have recently given birth. Other factors that can contribute to the condition include obesity, repetitive heavy lifting, and chronic coughing.
While diastasis recti is often considered a cosmetic issue, it can also cause functional problems. Some people with the condition may experience back pain, pelvic floor dysfunction, and urinary or bowel problems.
However, it is important to note that not everyone with diastasis recti will experience these symptoms.
Treatment for diastasis recti typically involves exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles and improve posture. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the separation.
It is important to seek the advice of a healthcare professional if you suspect you may have diastasis recti, as they can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Causes of Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is a condition that occurs when the rectus abdominis muscles separate, creating a gap in the abdominal wall. This gap can cause a bulge in the middle of the abdomen and can lead to various complications, including bowel problems.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of diastasis recti. One of the most common causes is pregnancy. As the uterus expands during pregnancy, it puts pressure on the abdominal muscles, which can cause them to separate.
Pregnant women who gain a significant amount of weight or carry multiple fetuses, such as twins or triplets, are at an increased risk of developing diastasis recti.
Another contributing factor is obesity. Excess body weight can put a strain on the abdominal muscles, causing them to weaken and separate. Additionally, heavy lifting and straining during bowel movements can also contribute to the development of diastasis recti.
Hormones can also play a role in the development of diastasis recti. During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that relax the muscles and ligaments in preparation for childbirth. This relaxation can cause the abdominal muscles to separate more easily.
In summary, diastasis recti can be caused by a combination of factors, including pregnancy, weight gain, obesity, twins or triplets, heavy lifting, and hormones.
It is important to take steps to prevent the condition, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and practicing good posture.
Symptoms of Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is a condition that can cause a range of symptoms. Some people with diastasis recti may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may experience a combination of symptoms that can be quite uncomfortable.
One of the most common symptoms of diastasis recti is a bulge or ridge that appears in the middle of the abdomen. This bulge may be more noticeable when the person is standing or doing certain activities, such as lifting heavy objects or doing crunches.
In addition to the bulge, some people with diastasis recti may experience bloating or poor posture. This can be due to the weakened abdominal muscles, which can make it difficult to maintain good posture and can also contribute to digestive issues.
Another symptom of diastasis recti is lower back pain. This is often due to the weakened muscles in the abdomen, which can cause the back muscles to work harder to compensate.
Some people with diastasis recti may also experience coning or doming of the abdominal muscles, which can be seen when the person is doing certain exercises or activities.
It’s important to note that not everyone with diastasis recti will experience all of these symptoms, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
If you suspect that you may have diastasis recti, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diastasis Recti and Bowel Problems
Diastasis recti is a condition that occurs when the abdominal muscles separate, causing a bulge in the middle of the abdomen.
While it is commonly associated with pregnancy, it can also occur in men and women who have never been pregnant. In some cases, diastasis recti can cause bowel problems.
Constipation is a common issue that diastasis recti can contribute to. When the abdominal muscles are weakened and separated, it can be difficult to pass stool. This can lead to constipation, which can cause discomfort, bloating, and other digestive issues.
Incontinence is another potential bowel problem associated with diastasis recti. When the abdominal muscles are weak, it can be difficult to control the muscles that control bowel movements. This can lead to incontinence, which can be embarrassing and uncomfortable.
Pelvic floor dysfunction is also commonly associated with diastasis recti. The pelvic floor muscles are responsible for supporting the bladder, uterus, and rectum. When the abdominal muscles are weak and separated, it can put additional strain on the pelvic floor muscles.
This can lead to pelvic floor dysfunction, which can cause a range of symptoms, including bowel problems.
Straining during bowel movements is another potential issue for people with diastasis recti. When the abdominal muscles are weak, it can be difficult to generate the necessary force to pass stool.
This can lead to straining, which can cause additional pressure on the abdominal muscles and worsen the condition.
Overall, while diastasis recti can contribute to bowel problems, it is important to note that not everyone with the condition will experience these issues.
If you are experiencing bowel problems, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosis of Diastasis Recti
Diagnosing diastasis recti typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider or a physical therapist. The examination may involve measuring the distance between the rectus abdominis muscles using finger widths or a measuring tape.
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition. These tests can provide a more detailed view of the abdominal muscles and the extent of the separation.
It is important to note that not all cases of diastasis recti are symptomatic, and some individuals may not even be aware that they have the condition.
However, if symptoms such as bowel problems or back pain are present, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Overall, a thorough physical examination and, if necessary, imaging tests can help diagnose diastasis recti and guide treatment decisions. Physical therapists can also provide valuable guidance and treatment options for individuals with diastasis recti.
Treatment and Management of Diastasis Recti
The treatment and management of diastasis recti depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, conservative treatment options may be recommended, such as exercise and supportive garments.
One of the most common forms of treatment for diastasis recti is exercise. Core strengthening exercises, such as Pilates and yoga, can be effective in reducing the gap between the abdominal muscles.
Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the core muscles and improve posture.
Supportive garments, such as abdominal binders and compression garments, can be used to provide additional support to the abdominal muscles and help reduce the appearance of a protruding belly.
These garments can also be worn during exercise to provide additional support to the core muscles.
In more severe cases of diastasis recti, surgery may be recommended. Abdominoplasty, also known as a tummy tuck, is a surgical procedure that can be used to repair the abdominal muscles and remove excess skin and fat.
This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have significant abdominal muscle separation and excess skin and fat in the abdominal area.
It is important to note that while exercise and supportive garments can be effective in reducing the appearance of diastasis recti, they may not be able to fully repair the abdominal muscles. In some cases, surgery may be the best option for achieving optimal results.
Overall, the treatment and management of diastasis recti should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. A healthcare professional can help determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health and fitness level.
Diastasis Recti in Men
Diastasis recti is a condition that is commonly associated with women who have gone through pregnancy. However, men can also develop this condition, especially those who engage in weightlifting or yo-yo dieting.
Diastasis recti in men occurs when the abdominal muscles separate, causing a bulge in the middle of the abdomen. This can result in a weakened core, which can lead to back pain and poor posture.
Men who lift heavy weights may be more prone to developing diastasis recti due to the strain placed on their abdominal muscles. Yo-yo dieting, which involves rapid weight gain and loss, can also contribute to the development of this condition.
It is important for men to be aware of the symptoms of diastasis recti, such as a protruding belly, lower back pain, and poor posture. Treatment options may include physical therapy, exercises to strengthen the core muscles, and in severe cases, surgery.
Overall, while diastasis recti is more commonly associated with women, men can also develop this condition. It is important for men to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms associated with diastasis recti and to seek treatment if necessary.
Diastasis Recti and Pregnancy
Diastasis Recti is a common condition that affects many pregnant women. It is the separation of the rectus abdominis muscles along the midline of the body. This separation can occur during pregnancy due to the stretching of the abdominal muscles to accommodate the growing uterus.
During the third trimester, the uterus becomes very large and can put a lot of pressure on the abdominal muscles. This pressure can cause the muscles to separate, leading to Diastasis Recti.
Women who have had multiple pregnancies or who have carried large babies are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
After delivery, the postpartum period is a critical time for women with Diastasis Recti. The abdominal muscles need time to heal and come back together. Women who try to do too much too soon after delivery can delay the healing process and make the condition worse.
In addition to the physical discomfort that comes with Diastasis Recti, some women also experience bowel problems. The separation of the abdominal muscles can affect the function of the intestines, leading to constipation and other digestive issues.
It is important for women to be aware of the symptoms of Diastasis Recti and to take steps to prevent and treat the condition.
This may include exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, avoiding heavy lifting and other activities that can put strain on the muscles, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist.
Newborn babies can also be affected by Diastasis Recti. If the condition is severe, it can cause a visible bulge in the baby’s abdomen. However, most cases of Diastasis Recti in newborns are mild and do not require treatment.
Overall, Diastasis Recti is a common condition that affects many pregnant women. While it can be uncomfortable and lead to bowel problems, it can be prevented and treated with the right care and attention.
Complications of Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is a separation of the abdominal muscles that can occur during pregnancy or due to excessive strain on the abdominal muscles. While it is not a serious medical condition, it can cause complications in some cases.
One of the most common complications of diastasis recti is the development of a hernia. A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. This can cause pain, discomfort, and other symptoms.
Another potential complication of diastasis recti is prolapse, which occurs when the pelvic organs (such as the uterus or bladder) shift out of their normal position. This can cause discomfort, urinary incontinence, and other symptoms.
Umbilical hernias are also more common in people with diastasis recti. An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal muscles near the belly button. This can cause pain and discomfort, and may require surgery to repair.
Urinary incontinence is another potential complication of diastasis recti. This occurs when the muscles that control the bladder weaken, causing leakage or difficulty holding in urine.
Pelvic pain and weakened core muscles are also possible complications of diastasis recti. Pelvic pain can occur due to the shifting of pelvic organs, while weakened core muscles can lead to poor posture and difficulty with activities that require core strength.
Overall, while diastasis recti is not a serious medical condition, it can lead to complications in some cases. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience any symptoms or concerns related to diastasis recti.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing diastasis recti is important, especially for those who are at higher risk due to pregnancy or certain physical activities. Making lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Maintaining a strong core and body is essential to preventing diastasis recti. Engaging in gentle movements that do not put too much pressure on the belly and pelvic floor can be helpful.
It is also important to keep the feet flat on the ground and shoulders relaxed during exercise and daily activities.
Individuals who are pregnant or have given birth should work with a healthcare provider to develop a safe exercise plan that supports the pelvic floor and connective tissue. It is important to avoid exercises that cause discomfort or strain on the abdomen.
In addition to exercise, maintaining a healthy diet and weight can also reduce the risk of developing diastasis recti. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients can support the body’s healing process and strengthen the connective tissue.
Other risk factors for diastasis recti include chronic constipation and heavy lifting. Addressing these factors through lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Overall, preventing diastasis recti requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and gentle movements that support the body. Working with a healthcare provider can provide additional guidance on preventing and managing this condition.
Also, read some related posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can diastasis recti cause IBS?
There is no direct evidence that shows a causal relationship between diastasis recti and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, some people with diastasis recti may experience symptoms similar to IBS, such as constipation, bloating, and abdominal pain.
Does diastasis recti cause gas?
Diastasis recti may contribute to the development of gas, as it can affect the proper functioning of the abdominal muscles. Weakened abdominal muscles may lead to poor digestion and the buildup of gas in the intestines.
What does diastasis recti pain feel like?
Diastasis recti pain can feel like a dull ache or pressure in the abdominal area. It may worsen during physical activity or when lifting heavy objects. Some people may also experience pain during bowel movements or sexual intercourse.
Can diastasis recti cause nausea?
Diastasis recti is not typically associated with nausea. However, if the condition is severe and causes significant discomfort, it may indirectly lead to nausea or vomiting.
Can diastasis recti cause pain under ribs?
Diastasis recti may cause pain under the ribs if the separation of the abdominal muscles is severe enough to affect the surrounding structures, such as the diaphragm or ribcage.
Can diastasis recti cause bloating?
Diastasis recti can contribute to bloating, as it can affect the proper functioning of the abdominal muscles and lead to poor digestion. Bloating may be more pronounced after meals or during physical activity.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.