It’s common for women to experience a range of physical and emotional symptoms during the first trimester of pregnancy.
However, what happens when these symptoms seem to disappear or lessen? Is it normal to sometimes not feel pregnant in the first trimester?
The answer is yes. While some women may experience intense symptoms throughout their entire pregnancy, others may have a more mild experience, with symptoms coming and going.
This can be due to a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, individual differences in pregnancy experiences, and more.
Understanding the First Trimester:
- Experiencing a range of symptoms during the first trimester is common, but the intensity and duration can vary.
- Women may experience a reduction or disappearance of symptoms during the first trimester, which is also normal.
- The fluctuation of symptoms can be attributed to hormonal changes and individual differences in pregnancy experiences.
Understanding the First Trimester
The first trimester of pregnancy is a crucial time for both the mother and the baby. It is a period of rapid growth and development for the fetus, and it can also be a time of significant physical and emotional changes for the mother.
The first trimester begins on the first day of the last menstrual period and lasts until the end of week 12 of pregnancy. During this time, the baby is referred to as an embryo until the end of week 10, after which it is called a fetus.
One of the most significant milestones of the first trimester is implantation, which occurs around 6-10 days after ovulation. This is when the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus and begins to grow.
Pregnancy symptoms can begin as early as a missed period, which is often the first sign of pregnancy. Other common symptoms of the first trimester include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, and frequent urination.
It is not uncommon for women to sometimes not feel pregnant during the first trimester, especially if they are not experiencing many symptoms.
However, it is important to note that every woman’s pregnancy is different, and some may experience more symptoms than others.
Due dates are typically calculated based on the first day of the last menstrual period, and the estimated due date is usually around 40 weeks from that date.
However, this can vary depending on the length of a woman’s menstrual cycle and the timing of ovulation and conception.
Overall, the first trimester is a critical time in pregnancy, and it is important for women to take care of themselves and their growing baby. This includes getting regular prenatal care, eating a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and getting plenty of rest.
Common Symptoms of Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a unique experience for every woman, and while some may experience a variety of symptoms, others may have none at all.
However, there are some common physical and emotional symptoms that many women experience during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Physical Symptoms
Nausea and Vomiting
One of the most common symptoms of pregnancy is nausea and vomiting. This is often referred to as morning sickness, although it can occur at any time of the day.
Morning sickness usually begins around the sixth week of pregnancy and can last until the 12th week. However, some women may experience it throughout their entire pregnancy.
Fatigue
Feeling tired is another common symptom of pregnancy. This is due to the increased levels of progesterone in the body, which can cause drowsiness. It is important for pregnant women to get plenty of rest and to listen to their body’s needs.
Cramping
Mild cramping is normal during the first trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the uterus stretching and growing to accommodate the growing fetus.
However, severe cramping or abdominal pain should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
Headaches
Headaches are also common during the first trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the changes in hormone levels and increased blood volume in the body.
Pregnant women should avoid taking over-the-counter pain medications and instead try natural remedies like drinking plenty of water, getting rest, and applying a cold compress to the forehead.
Food Cravings and Aversions
Many pregnant women experience cravings for certain foods, while others may experience aversions to certain foods. This is due to the changes in hormone levels and can be managed by eating a well-balanced diet and listening to the body’s needs.
Emotional Symptoms
Mood Swings
Pregnancy can also cause mood swings due to the changes in hormone levels. Pregnant women may feel happy one moment and then suddenly become sad or irritable. It is important for women to talk to their healthcare provider if they are experiencing severe mood swings.
Anxiety
Feeling anxious or worried during pregnancy is also common. This is due to the anticipation of the upcoming changes in life and the responsibility of caring for a new life. Pregnant women should talk to their healthcare provider if they are experiencing severe anxiety or panic attacks.
In conclusion, while every woman’s pregnancy experience is unique, there are common physical and emotional symptoms that many women experience during the first trimester.
It is important for pregnant women to listen to their body’s needs and to seek medical attention if they are experiencing severe symptoms.
Medical Care During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, medical care is crucial to ensure the health of the pregnant person and the developing fetus. Regular checkups and prenatal care are essential to monitor the progress of the pregnancy and detect any potential issues early on.
Routine Checkups
Pregnant individuals should schedule regular checkups with their healthcare provider, whether it be a doctor, midwife, or obstetrician.
These checkups typically occur once a month in the first and second trimesters and then more frequently in the third trimester.
During these appointments, the healthcare provider will monitor the pregnant person’s weight, blood pressure, and urine, and listen to the fetal heartbeat.
They may also perform additional tests, such as blood work and ultrasounds, to ensure the pregnancy is progressing normally.
Prenatal Care and Vitamins
Prenatal care is essential for the health of both the pregnant person and the developing fetus. Prenatal care includes regular checkups, as well as taking prenatal vitamins.
Prenatal vitamins contain essential nutrients, such as folic acid, iron, and calcium, that are crucial for fetal development. Pregnant individuals should discuss their prenatal vitamin needs with their healthcare provider.
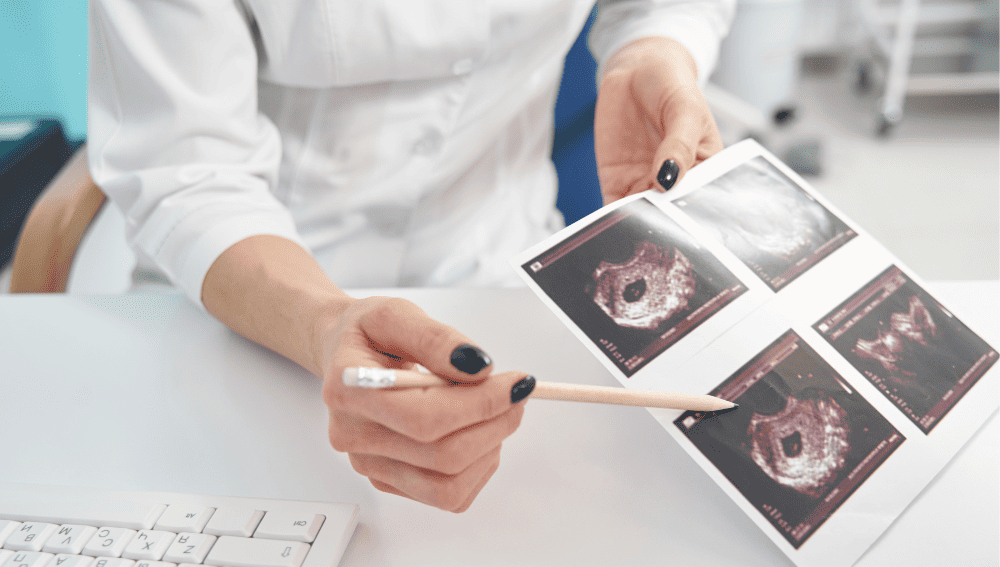
Ultrasound and Screening
Ultrasound and screening tests are important components of prenatal care. Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images of the fetus, allowing healthcare providers to monitor fetal growth and development.
Early ultrasounds can also help determine the estimated due date (EDD). Screening tests, such as blood tests and genetic tests, can help identify potential issues with the pregnancy, such as chromosomal abnormalities or neural tube defects.
In conclusion, medical care during pregnancy is essential to ensure the health of both the pregnant person and the developing fetus. Regular checkups, prenatal care, and ultrasound and screening tests are all important components of medical care during pregnancy.
Pregnant individuals should discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure they receive appropriate medical attention throughout their pregnancy.
Understanding Hormonal Changes
During the first trimester of pregnancy, many women experience a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity and frequency.
Some women may feel pregnant all the time, while others may not feel pregnant at all. Understanding the hormonal changes that occur during this time can help explain why some women may not feel pregnant in the first trimester.
Pregnancy hormones, such as progesterone and estrogen, play a crucial role in the early stages of pregnancy. These hormones are responsible for preparing the body for pregnancy and helping to maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Progesterone, for example, helps thicken the lining of the uterus, making it easier for the fertilized egg to implant and grow. Estrogen, on the other hand, helps maintain the pregnancy by promoting blood flow to the uterus and supporting the growth and development of the fetus.
Hormone levels can vary from woman to woman and can also fluctuate throughout the day. Some women may experience higher levels of hormones, which can lead to more intense symptoms, while others may have lower levels, which can result in fewer symptoms.
Additionally, some women may be more sensitive to hormonal changes than others, which can also impact how they feel during the first trimester.
Another hormone that plays a crucial role in early pregnancy is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is produced by the placenta and helps support the growth and development of the fetus.
hCG levels can vary greatly from woman to woman, and can also fluctuate throughout the day. Higher levels of hCG are typically associated with more intense symptoms, while lower levels may result in fewer symptoms.
In conclusion, hormonal changes during the first trimester of pregnancy can vary greatly from woman to woman and can impact how they feel during this time.
Understanding these changes can help women better understand their symptoms and what to expect during the early stages of pregnancy.
Changes in Body Functions
During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes many changes. Some of these changes may not be noticeable, while others can be quite obvious. In this section, we will discuss the changes that occur in the digestive and urinary systems.
Digestive System Changes
Many women experience changes in their digestive system during the first trimester of pregnancy. These changes can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Heartburn
- Increased appetite
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of early pregnancy, often referred to as morning sickness. This is caused by hormonal changes in the body, and can be triggered by certain smells or foods.
Constipation is also common, as the digestive system slows down to allow more nutrients to be absorbed by the body. Heartburn can occur due to the relaxation of the muscles in the esophagus, which allows stomach acid to flow back up into the throat.
Finally, many women experience an increased appetite as their body requires more nutrients to support the developing fetus.
Urinary System Changes
The urinary system also undergoes changes during the first trimester of pregnancy. These changes can include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Changes in the kidneys
Frequent urination is common during early pregnancy, as the uterus expands and puts pressure on the bladder. This can be inconvenient, but it is a normal part of the process.
However, pregnant women are also at an increased risk of developing UTIs, which can be dangerous if left untreated. It is important to drink plenty of fluids and practice good hygiene to prevent UTIs.
Finally, the kidneys undergo changes during pregnancy to help filter waste products from the body and support the developing fetus. This can cause changes in urine output and color, but is generally not a cause for concern.
Overall, changes in the digestive and urinary systems are a normal part of pregnancy. While they can be uncomfortable, most women find that these symptoms improve as they move into the second trimester.
Concerns and Complications
During the first trimester, some women may experience periods where they do not feel pregnant. While this is normal, it can also be a cause for concern for some women. In this section, we will discuss some of the concerns and complications that may arise during the first trimester.
Miscarriage and Bleeding
One of the most significant concerns for women during the first trimester is the risk of miscarriage. Miscarriages occur in about 10-20% of all pregnancies, and most occur in the first trimester.
Bleeding is a common symptom of miscarriage, but not all bleeding during pregnancy leads to a miscarriage.
If a woman experiences bleeding during the first trimester, it is essential to contact their healthcare provider immediately. They will perform an ultrasound to determine if the pregnancy is viable.
If the pregnancy is viable, the healthcare provider will monitor the woman closely for any signs of complications.
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG) is a severe form of morning sickness that affects about 1-2% of pregnant women.
Women with HG experience severe nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration and weight loss. HG can be a cause for concern as it can lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances and liver damage.
If a woman is experiencing severe nausea and vomiting during the first trimester, it is essential to contact their healthcare provider. They may prescribe medication or recommend dietary changes to help manage the symptoms.
In conclusion, while it is normal to sometimes not feel pregnant during the first trimester, it is essential to be aware of the potential concerns and complications that may arise. Women should contact their healthcare provider if they experience any worrying symptoms such as bleeding, cramps, fever, or anxiety.
Pregnancy and Covid-19 Vaccine
Many pregnant women have concerns about receiving the Covid-19 vaccine during their pregnancy. The vaccine was not tested on pregnant women during the clinical trials, so there is limited information about its safety and efficacy in this population.
However, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) now recommend that pregnant women receive the vaccine.
The decision to get vaccinated should be based on an individual’s risk of exposure to Covid-19, the potential benefits and risks of vaccination, and the woman’s personal preferences.
Pregnant women who are at high risk of exposure to Covid-19, such as healthcare workers or those with underlying medical conditions, may benefit from the vaccine.
It is important to note that there have been no reports of adverse pregnancy outcomes among women who received the Covid-19 vaccine during pregnancy.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of the vaccine on pregnancy and fetal development.
In addition, it is recommended that pregnant women discuss their decision to receive the vaccine with their healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and answer any questions about the vaccine’s safety and potential risks.
Overall, while there is limited information about the safety and efficacy of the Covid-19 vaccine in pregnant women, the current recommendations from ACOG and the CDC suggest that the benefits of vaccination may outweigh the potential risks for some pregnant women.
The Second and Third Trimester
As the pregnancy progresses into the second trimester, the fetus grows rapidly and the mother’s body undergoes significant changes. By this point, most women will feel pregnant and experience typical pregnancy symptoms such as weight gain, increased appetite, and fatigue.
During the second trimester, the fetus’s organs continue to develop, and the mother may start to feel movement as the baby becomes more active. The placenta also continues to grow and provide vital nutrients to the developing fetus.
In the third trimester, the fetus becomes even more active, and the mother’s body prepares for childbirth. The mother may experience more discomfort as the baby grows and puts pressure on her organs.
She may also experience Braxton Hicks contractions, which are practice contractions that help prepare the body for labor.
As the due date approaches, the mother may experience more frequent and intense contractions, signaling the onset of labor. Once the baby is born, the placenta is expelled from the mother’s body, and the newborn begins to adjust to life outside the womb.
Overall, it is normal to feel less pregnant in the first trimester when symptoms may be mild or nonexistent. As the pregnancy progresses into the second and third trimesters, the mother and fetus undergo significant changes, and typical pregnancy symptoms become more pronounced.
Lifestyle and Pregnancy
Exercise and Pregnancy
Staying active during pregnancy can have numerous benefits for both the mother and baby. Regular exercise can help with weight management, reduce the risk of gestational diabetes, and improve overall mood and energy levels.
However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting or continuing any exercise routine during pregnancy. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga are generally safe options.
Sleep and Pregnancy
Getting enough quality sleep during pregnancy can be a challenge due to hormonal changes, physical discomfort, and frequent urination.
However, getting adequate rest is crucial for both the mother and baby’s health and well-being. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, avoiding caffeine and large meals before bedtime, and using pillows for support can help improve sleep quality.
Diet During Pregnancy
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet during pregnancy is essential for the baby’s growth and development.
Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help ensure that both the mother and baby are getting the necessary vitamins and minerals. It is also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
It is important to note that every pregnancy is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidance on lifestyle choices during pregnancy.
Physical Changes
During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes many changes as it prepares to support the growth and development of the fetus.
Some women may not feel pregnant during this time, but physical changes are taking place nonetheless.
Breast Changes
One of the most noticeable changes during the first trimester is breast tenderness and enlargement. This is due to an increase in the hormone estrogen, which causes the milk ducts to grow and the breasts to become more sensitive. The areolas may also darken and become more prominent.
Blood Volume and Circulation Changes
The body’s blood volume increases by about 50% during pregnancy, which can cause changes in circulation.
This can lead to feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up quickly. It is important to stay hydrated and avoid standing for long periods of time to prevent these symptoms.
Changes in Bones and Nails
During pregnancy, the body absorbs more calcium from the diet to support the growth of the fetus. This can lead to changes in bone density and may increase the risk of osteoporosis later in life. Nails may also become brittle or grow more slowly due to hormonal changes.
Overall, physical changes during the first trimester of pregnancy are normal and necessary to support the growth and development of the fetus. It is important to listen to your body and seek medical advice if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Understanding Pregnancy Tests
When a woman suspects she may be pregnant, one of the first things she may do is take a pregnancy test. These tests work by detecting the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta after a fertilized egg implants in the uterus.
There are two types of pregnancy tests: urine tests and blood tests. Urine tests are the most common type and can be done at home or at a doctor’s office. Blood tests are less commonly used and are usually done at a doctor’s office.
A negative pregnancy test means that no hCG was detected in the urine or blood sample. This can happen if the test was taken too early, before there is enough hCG in the body to be detected. It can also happen if the test was not done correctly or if the woman is not pregnant.
A positive pregnancy test means that hCG was detected in the urine or blood sample. This indicates that the woman is pregnant. False positives are rare, but they can happen if the woman is taking certain medications or has a medical condition that produces hCG.
It is important to note that a negative pregnancy test does not necessarily mean that a woman is not pregnant. It is possible for a woman to have a negative test result and still be pregnant, especially if the test was taken too early.
If a woman suspects she may be pregnant but has a negative test result, she should wait a few days and take another test or see a doctor for a blood test.
In summary, pregnancy tests are an important tool for women who suspect they may be pregnant. Understanding how they work and what the results mean can help women make informed decisions about their health and pregnancy.
Health Insurance and Pregnancy
Health insurance is an important consideration during pregnancy. It is essential to have adequate coverage to ensure that all medical expenses are covered, especially if complications arise during pregnancy or delivery.
Most health insurance policies cover prenatal care, childbirth, and postnatal care. However, it is important to check the policy details to ensure that all necessary services are covered. Some policies may not cover certain procedures or treatments, so it is important to understand the limitations of the policy.
It is also important to check whether the policy covers the cost of medications and supplements that may be required during pregnancy. Some policies may cover only generic medications, while others may cover brand-name medications as well.
In some cases, health insurance policies may not cover the cost of certain tests or procedures that are considered elective, such as genetic testing. It is important to understand what is covered under the policy and what is not, to avoid any unexpected expenses.
In conclusion, it is important to have adequate health insurance coverage during pregnancy. It is essential to understand the policy details and limitations, to ensure that all necessary services are covered.
The Role of Midwives
Midwives play an essential role in supporting pregnant women throughout their pregnancy, especially during the first trimester.
They are trained professionals who provide guidance, education, and emotional support to women during this critical time. Midwives are often the first point of contact for women who have questions or concerns about their pregnancy.
During the first trimester, many women may not feel pregnant, which can be a source of anxiety and worry. Midwives can help alleviate these concerns by providing information about common symptoms and reassuring women that it is normal not to feel pregnant during this time.
They can also offer advice on ways to manage symptoms, such as nausea and fatigue.
Midwives can also play a vital role in identifying potential complications early on. They monitor the health of both the mother and the baby, and they can detect any issues that may arise.
If any concerns arise, they can refer women to an obstetrician or other medical professional for further evaluation and treatment.
In addition to providing medical care, midwives also offer emotional support to women during this time. They understand that pregnancy can be a challenging and emotional experience, and they are there to listen, offer advice, and provide encouragement.
They can also help women prepare for childbirth and provide education on breastfeeding and other postpartum issues.
Overall, midwives play a critical role in supporting women throughout their pregnancy, especially during the first trimester. They provide a range of services, including medical care, emotional support, and education, and they are an essential part of the healthcare team.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you be pregnant without any symptoms?
It is possible for some women to be pregnant without experiencing any noticeable symptoms. Every woman’s body is different, and some may not experience the typical symptoms such as morning sickness, fatigue, or breast tenderness.
When do pregnancy symptoms stop in the first trimester?
Pregnancy symptoms can vary from woman to woman and can last for different lengths of time. In general, many women begin to experience relief from symptoms around the 12th week of pregnancy.
However, some women may continue to experience symptoms throughout their pregnancy.
Is it normal for pregnancy symptoms to come and go?
Yes, it is normal for pregnancy symptoms to come and go. Hormonal changes can cause symptoms to fluctuate or even disappear for a period of time. However, if you experience any unusual symptoms or have concerns, it is always best to consult with your healthcare provider.
Is it possible to be 9 weeks pregnant with no symptoms?
Yes, it is possible to be 9 weeks pregnant with no noticeable symptoms. As mentioned earlier, every woman’s body is different, and some may not experience symptoms until later in their pregnancy.
What are the signs that you are still pregnant?
The best way to confirm that you are still pregnant is to have an ultrasound or other medical testing. However, some common signs that you are still pregnant include missed periods, positive pregnancy tests, and continued growth of the uterus.
Is it common to not feel pregnant at 12 weeks?
It is not uncommon for some women to not feel pregnant at 12 weeks. As mentioned earlier, every woman’s body is different, and some may not experience noticeable symptoms until later in their pregnancy.
However, if you have concerns or questions, it is always best to consult with your healthcare provider.
Learn more from another post: 12 Weeks Pregnant Belly Not Hard

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.