Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn babies. It contains all the necessary nutrients and antibodies needed for a baby’s growth and development. But have you ever wondered why you can’t shake breast milk?
Understanding Breast Milk Breast milk is a complex fluid that contains fat, protein, and other nutrients that are important for a baby’s growth. It also contains immune cells and antibodies that help protect the baby from infections and illnesses. When breast milk is expressed, it separates into layers, with the fat rising to the top.
The Impact of Shaking Breast Milk Shaking breast milk can cause the fat to break down and mix with the other components of the milk, making it less nutritious for the baby. It can also cause air bubbles to form, which can lead to gas and discomfort for the baby. So, why can’t you shake breast milk? The answer is simple: shaking breast milk can damage its nutritional value and make it less beneficial for the baby.
Key Takeaways
- Breast milk is a complex fluid that contains all the necessary nutrients and antibodies for a baby’s growth and development.
- Shaking breast milk can cause the fat to break down and mix with the other components, making it less nutritious for the baby.
- Proper handling and storage of breast milk can help preserve its nutritional value and ensure it is safe for the baby to consume.
Understanding Breast Milk
Breast milk is a complex and highly nutritious fluid that provides infants with all the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development. It is produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of lactating women and is specifically tailored to meet the nutritional needs of infants.
Breast milk contains a variety of proteins, nutrients, and other substances that are essential for the growth and development of infants. These include macronutrients such as fats, carbohydrates, and proteins, as well as micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. Breast milk also contains immune system cells, hormone growth factors, and other substances that help support the infant’s developing immune system.
The nutritional value of breast milk is unparalleled, and it is the perfect food for infants during the first six months of life. Breast milk contains a unique combination of nutrients that cannot be replicated in formula or other artificial sources of nutrition. The fat content of breast milk is also highly variable and changes throughout the day and over time, providing infants with the necessary energy to grow and develop.
Breast milk also contains living cells, including fat globules and white blood cells, which help support the infant’s immune system. These cells help protect the infant from infections and other illnesses, and they also help promote the development of a healthy gut microbiome.
In summary, breast milk is a highly nutritious and complex fluid that provides infants with all the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development. It contains a variety of proteins, nutrients, and other substances that are essential for the development of the infant’s immune system and overall health.
The Impact of Shaking Breast Milk
Shaking breast milk is a common practice for mixing the layers of the milk. However, it has been found that shaking breast milk can have a negative impact on the quality of the milk.

When breast milk is shaken, it creates air bubbles that can cause the milk to denature or separate. Denaturing occurs when the protein structure of the milk is broken down by the shearing force of shaking. This can cause the milk to lose some of its nutritional value and may also affect the taste and texture of the milk.
Shaking breast milk can also damage the fat globules in the milk, which are responsible for providing energy to the baby. These fat globules can be sheared or agitated during the shaking process, which can cause them to break apart and form smaller droplets. This can make it harder for the baby to digest the milk and can also affect the absorption of nutrients.
Gentle swirling, on the other hand, is a better alternative to shaking breast milk. Swirling the milk helps to mix the layers without creating air bubbles or agitating the milk. This method helps to preserve the nutritional value of the milk and maintain its natural shape and consistency.
In conclusion, shaking breast milk can denature and damage the milk, affecting its nutritional value and taste. Gentle swirling is a better alternative for mixing breast milk without compromising its quality.
Proper Handling and Storage of Breast Milk
Proper handling and storage of breast milk is crucial to ensure that it remains safe and nutritious for your baby. Here are some guidelines to follow:
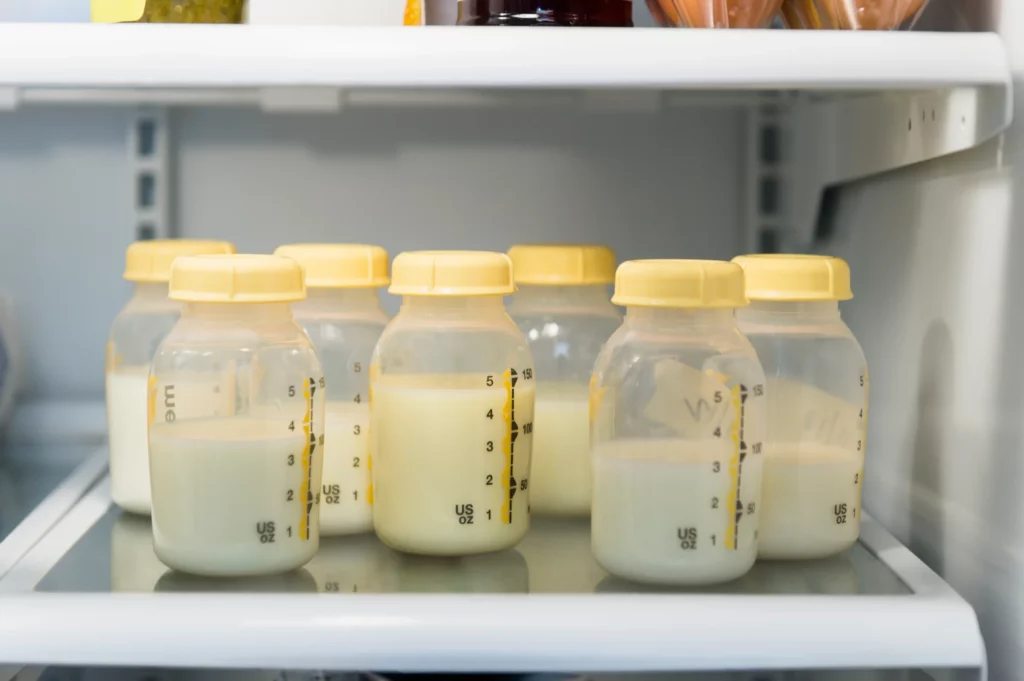

1. Pumping and Storing Breast Milk
When pumping breast milk, it is important to use a clean and sterilized pump. After pumping, the milk should be immediately transferred to a clean and sealed container. Make sure to label the container with the date and time the milk was expressed.
Stored breast milk should be kept in a refrigerator or freezer as soon as possible. If you are storing breast milk in a refrigerator, it should be kept at a temperature of 40°F (4°C) or below. If you are storing breast milk in a freezer, it should be kept at a temperature of 0°F (-18°C) or below.
2. Sealed Containers
Breast milk should be stored in a clean, sealed container. This helps to prevent contamination and maintain the quality of the milk. You can use plastic or glass containers that are specifically designed for storing breast milk. Make sure to leave some space at the top of the container to allow for expansion when freezing.
3. Leftover Breast Milk
If your baby does not finish a bottle of breast milk, the leftover milk should be discarded. Breast milk should not be reheated or reused once it has been fed to your baby.
4. Bottle Warmers
If you need to warm up stored breast milk, you can use a bottle warmer. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using a bottle warmer. You can also warm up breast milk by placing the container in warm water.
5. Deep Freezer
If you are storing breast milk for a longer period of time, such as for donation or future use, you can use a deep freezer. Breast milk can be stored in a deep freezer for up to 12 months.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your baby receives safe and nutritious breast milk.
Warming and Thawing Breast Milk
When it comes to warming and thawing breast milk, there are a few things to keep in mind to ensure the milk remains safe and healthy for your baby.
One common method is to place the breast milk bottle or bag in a bowl of warm water. This allows the milk to gradually warm up without being exposed to high temperatures that can destroy its nutrients. It’s important to note that the water should not be too hot, as this can cause the milk to overheat and form hot spots.
Another option is to use a bottle warmer specifically designed for breast milk. These devices warm the milk to a safe temperature and can help prevent hot spots from forming.
It’s important to avoid using a microwave to warm breast milk, as this can cause uneven heating and destroy some of the milk’s nutrients. Additionally, microwaving breast milk can create hot spots that can burn your baby’s mouth.
When thawing frozen breast milk, it’s best to do so slowly in the refrigerator or in a bowl of warm water. Avoid using hot water or leaving the milk out at room temperature to thaw, as this can increase the risk of bacteria growth.
Once breast milk has been warmed or thawed, it should be used within a certain timeframe to ensure its safety and freshness. Warmed breast milk should be used within two hours, while thawed breast milk should be used within 24 hours if kept in the refrigerator.
Overall, taking the time to properly warm and thaw breast milk can help ensure that your baby receives the full benefits of this nutritious food.
Breast Milk vs. Formula
Breast milk is the natural food for infants and provides all the necessary nutrients for growth and development. Formula, on the other hand, is a synthetic substitute for breast milk and is made from cow’s milk or soy protein.
One of the main differences between breast milk and formula is the way they are produced. Breast milk is produced by the mother’s body and is tailored to the baby’s needs. Formula, on the other hand, is manufactured in a factory and is a standardized product.
Breast milk also contains antibodies and other immune-boosting substances that help protect the baby from infections and illnesses. Formula does not contain these substances and may not provide the same level of protection.
Another difference between breast milk and formula is the way they are digested. Breast milk is easily digested by the baby’s digestive system, while formula may take longer to digest. This can lead to differences in bowel movements and may affect the baby’s overall health.
It is also important to note that breast milk cannot be homogenized, while formula can. Homogenization is a process that breaks down the fat molecules in milk to make it easier to digest. However, this process is not necessary for breast milk as it is already in a form that is easily digestible for the baby.
Finally, breast milk cannot be reconstituted like formula can. Reconstituting is the process of adding water to formula to make it ready for consumption. Breast milk is already in the perfect form for the baby and does not need to be diluted.
In summary, breast milk and formula have significant differences in their production, composition, and digestion. While formula can be a suitable substitute for breast milk in certain situations, breast milk is still the best option for most infants.
Impact of Shaking on Newborns and Infants
Shaking breast milk can have a negative impact on the health of newborns and infants. When breast milk is shaken, it can cause excessive gas and change the pH balance of the milk, leading to gut lining inflammation and colic in infants.

Additionally, shaking breast milk can damage the white blood cells present in the milk, which play a crucial role in boosting the immune system of the baby. This can also affect the growth and development of infants.
Furthermore, excessive shaking can cause a suction effect, leading to the formation of bubbles and foam. This can change the physical appearance of the milk, making it look spoiled and unappetizing to the baby.
The gut microbiome of infants is also affected by shaking breast milk. The gut lining is lined with beneficial bacteria that help in digestion and absorption of nutrients. Shaking can damage these bacteria, leading to gut microbiome imbalance.
In conclusion, shaking breast milk can have a negative impact on the health of newborns and infants. It is recommended to gently swirl the milk to mix the fat and avoid excessive shaking.
Scientific Evidence and Myths
There are several myths surrounding the inability to shake breast milk, but what does scientific evidence say about this topic?
Firstly, it is a common belief that shaking breast milk can damage the quality of the milk and destroy its nutrients. However, studies have shown that shaking breast milk does not affect the quality or composition of the milk in any way. In fact, breast milk is quite resilient and can withstand the mechanical stress of shaking without any significant changes.
Another myth is that shaking breast milk can destroy stem cells and antibodies present in the milk. However, research has shown that shaking breast milk does not affect the presence of stem cells or antibodies in the milk. These important components of breast milk remain intact and are not affected by shaking.
There is also a belief that shaking breast milk can cause an increase in bacteria or inflammation in the milk. However, this is not supported by scientific evidence. While bacteria and inflammation can be present in breast milk, these factors are not caused by shaking and are not affected by it.
Finally, some people believe that shaking breast milk can cause physical damage to the milk, leading to the formation of clumps or lumps. However, this is not true. Shaking breast milk does not cause any physical damage to the milk, and any clumps or lumps that may form are due to other factors, such as changes in temperature or storage conditions.
In conclusion, scientific evidence shows that shaking breast milk does not affect the quality, composition, or presence of important components such as stem cells and antibodies. It also does not cause an increase in bacteria or inflammation, nor does it cause physical damage to the milk. Therefore, there is no reason to avoid shaking breast milk if it needs to be mixed or reconstituted.
Also, you might want to check out some related posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
How should breast milk be stored?
Breast milk should be stored in clean containers that have been sterilized. It is best to use glass or BPA-free plastic bottles or bags that are specifically designed for breast milk storage. The containers should be labeled with the date and time the milk was expressed. Breast milk can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 4 days or in the freezer for up to 6 months.
What is the proper way to swirl breast milk?
Swirling breast milk is a gentle way to mix the fat that may have separated during storage. To swirl breast milk, gently rotate the container in a circular motion until the milk is well-mixed. Do not shake the container vigorously as this can damage the nutrients and proteins in the milk.
What should I do if my baby didn’t finish a bottle of breast milk?
If your baby did not finish a bottle of breast milk, you can store the leftover milk in the refrigerator for up to 2 hours. If the milk has been at room temperature for more than 2 hours, it should be discarded. Do not mix fresh breast milk with leftover milk that has been previously warmed.
How should I warm up breast milk?
Breast milk can be warmed up by placing the container in a bowl of warm water or using a bottle warmer. Do not use a microwave to heat up breast milk as this can create hot spots that can burn your baby’s mouth. Once breast milk has been warmed, it should be used within 1 hour.
How long can refrigerated breast milk last?
Refrigerated breast milk can last up to 4 days in the refrigerator. It is important to store breast milk in the back of the refrigerator, where the temperature is the most consistent. If you are not sure if breast milk is still good, you can smell it to check for sour or rancid odors.
Why is shaking breast milk not recommended?
Shaking breast milk is not recommended because it can damage the nutrients and proteins in the milk. Vigorous shaking can also create bubbles that can lead to gas and colic in babies. Swirling breast milk is a gentler way to mix the fat that may have separated during storage.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.
