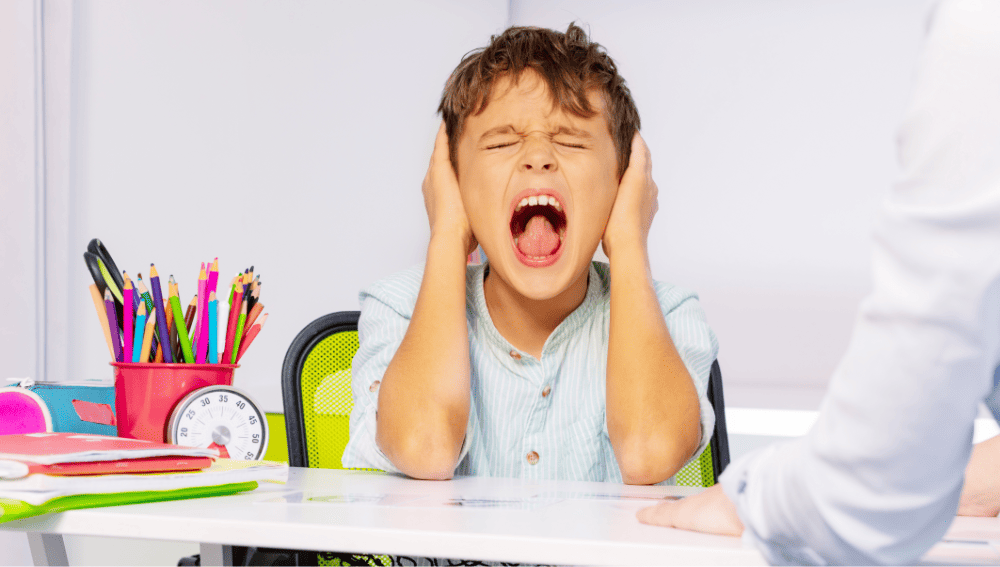
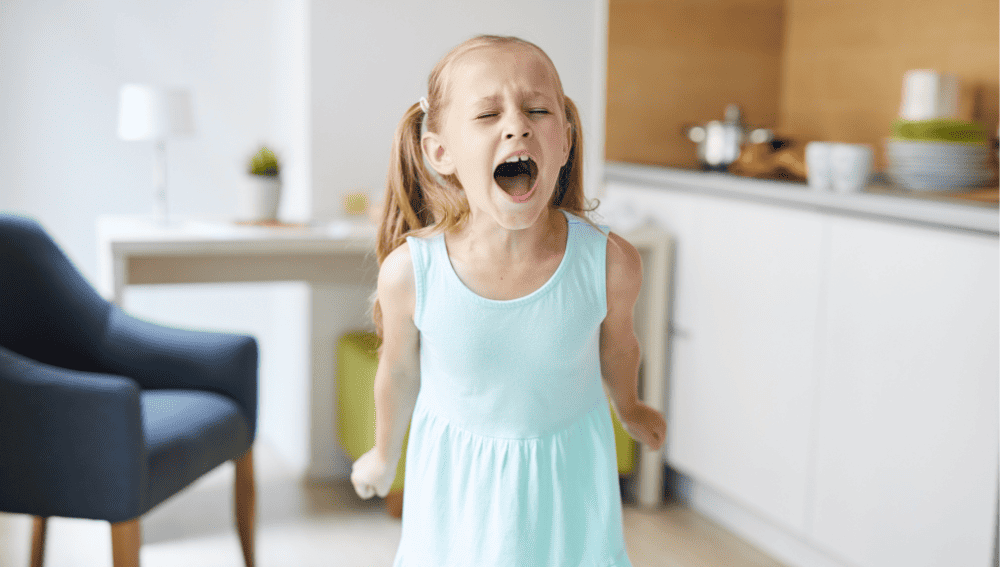
When a child begins acting out, it can be a cause for concern for parents and caregivers. Sudden behavior changes can be a sign of underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Understanding child behavior and identifying signs of acting out can help parents and caregivers take the necessary steps to support their child.
There can be many possible causes of sudden behavior changes in children. Stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on behavior, and changes in family dynamics or routine can also contribute to acting out.
Communication and cooperation between parents, caregivers, and the child can be crucial in identifying the root cause of the behavior and finding a solution.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding child behavior and identifying signs of acting out can help parents and caregivers address sudden behavior changes in their child.
- Stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on behavior, and changes in family dynamics or routine can also contribute to acting out.
- Communication and cooperation between parents, caregivers, and the child can be crucial in identifying the root cause of the behavior and finding a solution.
Understanding Child Behavior
Child behavior can be difficult to understand, especially if it seems to change suddenly. However, it is important to remember that behavior is a form of communication. Children may act out when they are feeling overwhelmed, stressed, or when they are unable to express their emotions in other ways.
Child development plays a crucial role in behavior. Young children may not have the language skills to express their feelings, which can lead to frustration and acting out. As children grow and develop, they learn new skills and ways to communicate, which can help reduce problem behavior.
It is also important to consider the child’s environment and experiences. Children who have experienced trauma or significant changes in their lives may be more likely to exhibit challenging behavior.
Additionally, children who are consistently exposed to stress or chaos may struggle with self-regulation and have difficulty controlling their behavior.
Early childhood is a critical time for social and emotional development. Children who are provided with a safe and nurturing environment, positive relationships, and opportunities to learn and play are more likely to develop healthy social and emotional skills.
Overall, understanding child behavior requires a holistic approach that considers the child’s development, experiences, and environment. By understanding the underlying reasons for a child’s behavior, parents and caregivers can provide appropriate support and help children develop healthy coping skills.
Identifying Signs of Acting Out
Acting out can be a sign of a child’s emotional distress, and it can be challenging for parents to identify the root cause of the behavior. However, by recognizing the signs of acting out, parents can take steps to address the issue and help their child.
Here are some common signs of acting out:
Physical Signs
Physical signs of acting out may include:
- Throwing objects
- Hitting or kicking
- Breaking things
- Running away from home or school
- Engaging in risky behavior
If a child is exhibiting these behaviors, it may be a sign that they are struggling with emotional issues and need support.
Emotional Signs
Emotional signs of acting out may include:
- Tantrums
- Screaming or crying
- Angry outbursts
- Defiance
- Refusal to follow rules or instructions
If a child is experiencing these emotional signs, it may be an indication that they are feeling overwhelmed or frustrated and need help processing their emotions.
Social Signs
Social signs of acting out may include:
- Difficulty getting along with peers
- Bullying or aggressive behavior towards others
- Isolation or withdrawal from social situations
- Disrespectful behavior towards authority figures
If a child is exhibiting these social signs, it may be a sign that they are struggling with social skills or feeling disconnected from others.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of acting out is an important step in helping a child who is struggling emotionally. By identifying the signs of acting out, parents can take steps to address the issue and provide support to their child.
Possible Causes of Sudden Behavior Changes
Sudden behavior changes in children can be concerning for parents and caregivers. It is important to identify the possible causes of such changes to address them effectively.
The following sub-sections explore some of the possible causes of sudden behavior changes in children.
Emotional Factors
Emotions can play a significant role in sudden behavior changes in children. Stress, anger, anxiety, and other emotional factors can trigger unexpected behavior in children.
Children may also act out when they are feeling overwhelmed or frustrated. It is essential to identify the underlying emotional factors and provide support to help the child manage their emotions.
Physical Factors
Physical factors such as hunger, tiredness, and sensory issues can also cause sudden behavior changes in children. Children may act out when they are hungry or tired, or when they are experiencing discomfort due to sensory issues.
It is important to ensure that the child’s basic physical needs are met, and any sensory issues are addressed.
Environmental Factors
Changes in the child’s environment can also cause sudden behavior changes. The arrival of a new baby, social circumstances, or changes in routine can all contribute to changes in behavior.
It is important to identify any environmental factors that may be contributing to the child’s behavior and provide support to help the child adjust.
In conclusion, sudden behavior changes in children can be caused by a variety of factors. Emotional, physical, and environmental factors can all play a role. It is important to identify the underlying causes and provide support to help the child manage their behavior effectively.
How Stress and Anxiety Affect Behavior
Stress and anxiety are common emotions that everyone experiences at some point in their lives. However, when children experience these emotions, it can cause them to act out in unexpected ways.
Understanding how stress and anxiety affect behavior can help parents and caregivers better support their children.
When a child is stressed or anxious, their body goes into “fight or flight” mode. This means that their body is preparing to either defend itself or run away from a perceived threat.
This response can cause physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and shaking. These physical symptoms can then lead to behavioral changes such as aggression, avoidance, or withdrawal.
Children who are anxious or worried may also have difficulty concentrating or completing tasks. They may become easily frustrated or irritable, and may have trouble sleeping or eating.
These behaviors can be particularly challenging for parents and caregivers to manage, as they can be disruptive to daily routines and activities.
It is important to note that not all children will exhibit the same behaviors when experiencing stress or anxiety. Some children may become more clingy or seek reassurance from adults, while others may become more withdrawn or avoidant.
It is important to pay attention to your child’s individual needs and behaviors, and to provide support and guidance as needed.
Parents and caregivers can help children manage stress and anxiety by teaching them coping strategies such as deep breathing, visualization, or mindfulness. It can also be helpful to create a calm and supportive environment at home, with consistent routines and clear expectations.
Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor may also be beneficial for children who are struggling with stress and anxiety.
Overall, understanding how stress and anxiety affect behavior can help parents and caregivers better support their children during challenging times.
By providing a safe and supportive environment, teaching coping strategies, and seeking professional help when needed, parents can help their children learn to manage their emotions and behaviors in healthy ways.
The Role of Communication and Cooperation
When a child starts acting out, it can be a sign that they are struggling with something. One possible reason for this behavior is a breakdown in communication and cooperation between the child and their caregivers.
Parents should make an effort to communicate with their child and understand their perspective. This involves active listening, asking open-ended questions, and validating their feelings. When a child feels heard and understood, they are more likely to cooperate and follow rules.
It is also important for parents to model good communication and cooperation. This means being consistent with rules and consequences, and avoiding blaming or shaming language. Instead, parents should focus on problem-solving and finding solutions together.
In some cases, a child may be acting out because they are seeking attention. In these situations, parents should make an effort to give their child positive attention when they are behaving well.
This can include spending quality time together, praising good behavior, and showing interest in their child’s activities and interests.
Blaming the child for their behavior is not productive and can damage the parent-child relationship. Instead, parents should focus on finding solutions and working together as a team. This can involve seeking outside help from a therapist or counselor if necessary.
Overall, good communication and cooperation are essential for maintaining a healthy parent-child relationship and addressing challenging behavior. By listening to their child, modeling positive behavior, and seeking solutions together, parents can help their child feel heard, understood, and supported.
Related: Ten Punishments That Work
Exploring the Aspect of Defiance
When a child starts acting out, one of the first things that parents and caregivers may notice is an increase in defiance. Defiance can manifest in a variety of ways, including refusing to follow rules or instructions, arguing with adults, and engaging in power struggles.
It can be frustrating for parents and caregivers, who may feel like their child is intentionally trying to make their lives difficult.
Defiance is a common behavior in children, and it is not always a sign of a serious problem. However, if a child’s defiance is persistent, severe, and interfering with their ability to function in daily life, it may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD).
Defiant behavior can be caused by a variety of factors, including a child’s temperament, their environment, and their experiences. Children who have experienced trauma, neglect, or abuse may be more likely to exhibit defiant behavior.
Additionally, children who have difficulty regulating their emotions or who struggle with anxiety or depression may be more likely to act out in defiant ways.
It is important for parents and caregivers to approach defiant behavior with patience and understanding. Punishing a child for their defiant behavior may only exacerbate the problem, and can lead to a cycle of negative behavior.
Instead, it is important to set clear boundaries and consequences for defiant behavior, while also providing positive reinforcement for positive behavior.
In some cases, seeking the help of a mental health professional may be necessary to address persistent and severe defiant behavior. A therapist can work with both the child and their caregivers to identify the underlying causes of the behavior and develop strategies for managing it.
The Impact of Power Shifts and Self-Esteem
Power shifts and self-esteem can have a significant impact on a child’s behavior. Children who feel powerless or have low self-esteem may act out to gain a sense of control or to get attention.
Power shifts can occur in various ways. For example, a child may experience a power shift when a new sibling is born, when a parent starts a new job, or when the family moves to a new home. These changes can be overwhelming for a child, and they may act out as a way to cope with the loss of control.
Similarly, self-esteem can play a role in a child’s behavior. Children with low self-esteem may act out to get attention or to feel better about themselves. They may also feel like they are not good enough and act out as a way to prove themselves.
It’s important for parents to understand the impact of power shifts and self-esteem on their child’s behavior. By recognizing these factors, parents can take steps to help their child feel more in control and build their self-esteem.
This can include setting clear boundaries, providing consistent routines, and praising their child’s efforts and accomplishments.
In some cases, professional help may be needed to address deeper issues related to power shifts and self-esteem. Parents should not hesitate to seek support from a therapist or counselor if they feel their child’s behavior is becoming unmanageable or if they have concerns about their child’s mental health.
Aggressive and antisocial behaviors can be concerning for parents, teachers, and caregivers alike. Children may display these behaviors for a variety of reasons, and it’s important to understand what may be causing these behaviors in order to address them appropriately.
Aggressive behavior can range from verbal aggression, such as yelling or name-calling, to physical aggression, such as hitting or biting.
Antisocial behavior can include lying, stealing, and breaking rules or laws. While some degree of these behaviors can be typical for children, if they persist or escalate, it may be a sign of a more serious issue.
One potential cause of aggressive or antisocial behavior is a lack of social and emotional skills. Children who struggle with communication, problem-solving, and emotional regulation may be more likely to act out in these ways.
Additionally, children who have experienced trauma or adverse childhood experiences may be more likely to display these behaviors.
In some cases, aggressive or antisocial behavior may be a symptom of a larger issue, such as a mental health condition like antisocial personality disorder. It’s important to note, however, that not all children who display these behaviors will have a diagnosis of a mental health condition.
Overall, understanding the potential causes of aggressive and antisocial behaviors can help parents, teachers, and caregivers address these issues in a way that is effective and supportive for the child.
By providing children with the skills and support they need to manage their emotions and behavior, it’s possible to help them develop into healthy, well-adjusted adults.
The Relevance of Medical History
The medical history of a child is an important factor to consider when trying to understand why they are acting out suddenly. Medical conditions such as anxiety disorder and mood disorder can be underlying causes of sudden changes in behavior.
Anxiety disorder can cause a child to feel nervous, fearful, and worried. These feelings can manifest in physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, and heart palpitations. Children with anxiety disorder may also have trouble sleeping, experience nightmares, and avoid social situations.
Mood disorder, on the other hand, can cause a child to experience extreme emotions such as sadness, anger, and irritability. These emotions can be intense and difficult to control, leading to sudden outbursts or other disruptive behaviors.
Children with mood disorder may also have trouble sleeping, experience changes in appetite, and have difficulty concentrating.
It is important for parents and caregivers to provide a detailed medical history of the child to their healthcare provider. This can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the child’s sudden change in behavior.
In addition, healthcare providers may conduct a physical examination and order laboratory tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions. If a medical condition is identified, appropriate treatment can be initiated to manage the symptoms and improve the child’s behavior.
Overall, understanding a child’s medical history is an important step in identifying the underlying cause of sudden changes in behavior. It is important to work with healthcare providers to ensure that any underlying medical conditions are identified and treated appropriately.
Role of a Child Psychologist
A child psychologist can play a crucial role in understanding and addressing sudden changes in a child’s behavior. Through psychotherapy and assessment, child psychologists can help identify underlying issues that may be causing the child to act out.
Psychotherapy involves talking with the child to explore their thoughts and feelings, and to help them develop coping strategies. This can help the child better manage their behavior and emotions, and improve their relationships with others.
Assessment may involve psychological testing, observation, and interviews with the child and their family. This can help the child psychologist gain a deeper understanding of the child’s behavior and any underlying issues that may be contributing to it.
Overall, the role of a child psychologist is to provide support and guidance to both the child and their family, and to work towards improving the child’s overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are many reasons why a child may start acting out suddenly. It could be due to changes in their environment, such as a new school or new home situation. It could also be due to changes in their family dynamic, such as the addition of a new sibling or a divorce.
Other factors that could contribute to sudden behavior changes include stress, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, children may act out due to a lack of attention or discipline at home, or due to exposure to negative influences such as peers or media.
It’s important to approach the situation with patience and understanding, and to try to identify any underlying causes for the behavior. Parents and caregivers can work with their child’s school or seek professional help if necessary.
By addressing the root causes of the behavior and providing a supportive and structured environment, parents and caregivers can help their child overcome their sudden acting out and develop healthy coping mechanisms for the future.
Also, do not miss to check out our post on How Will I Know If My Child Has Trouble Hearing
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common reasons for sudden changes in a child’s behavior?
There are many reasons why a child’s behavior may suddenly change. Some common reasons include stress at home or school, changes in routine or environment, illness or medication side effects, and developmental changes.
It is important to try to identify the underlying cause of the behavior change in order to address it effectively.
How can I tell if my child’s behavior is a cause for concern?
It is normal for children to have occasional outbursts or misbehavior, but if your child’s behavior is persistent, severe, or interfering with their daily life, it may be a cause for concern.
Some signs to look out for include aggression, defiance, withdrawal, changes in sleep or appetite, and academic or social problems.
What are some effective strategies for addressing sudden changes in a child’s behavior?
Effective strategies for addressing sudden changes in a child’s behavior include setting clear expectations and consequences, providing positive reinforcement for good behavior, using active listening and empathy to understand your child’s perspective, and modeling appropriate behavior yourself.
It is also important to seek support from family, friends, or professionals if needed.
What are some common triggers for misbehavior in children?
Common triggers for misbehavior in children include feeling overwhelmed or frustrated, being hungry or tired, feeling ignored or neglected, and feeling anxious or stressed. It is important to try to identify the trigger in order to address the behavior effectively.
How can I help my child regulate their emotions and behavior?
Helping your child regulate their emotions and behavior involves teaching them coping skills such as deep breathing, positive self-talk, and mindfulness. It is also important to help them identify and express their emotions in a healthy way, and to provide a safe and supportive environment for them to do so.
When should I seek professional help for my child’s behavior issues?
If your child’s behavior is persistent, severe, or interfering with their daily life, it may be time to seek professional help. Some signs that it may be necessary include self-harm, aggression towards others, substance abuse, or academic or social problems.
It is important to seek help from a qualified mental health professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Here’s a quick video explaining more reasons why your child may be acting up
Related Post: My Son is Obsessed With His Girlfriend!

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.