Pregnancy is a complex and delicate process, and expecting parents often wonder about the health and well-being of their developing fetus. One concern that may arise is the possibility of a fetal heartbeat disappearing and reappearing during gestation.
This topic warrants discussion and further understanding to address the questions and anxieties that parents-to-be may have.
A fetal heartbeat typically becomes detectable around six weeks into pregnancy and serves as a marker of fetal health. It is not uncommon for the heartbeat to fluctuate slightly, but the question remains: can a fetal heartbeat actually disappear and later reappear?
This article will explore possible reasons for the phenomenon of a fetal heartbeat disappearing and reappearing, as well as the role that medical procedures and the mother’s body may play in this process.
Key Takeaways
- Fetal heartbeat serves as an indicator of fetal health, typically detectable around six weeks into pregnancy
- The phenomenon of a disappearing and reappearing fetal heartbeat may be attributed to several factors
- Medical procedures, the mother’s body, and other circumstances can impact the detection of a fetal heartbeat
Understanding Fetal Heartbeat
A fetal heartbeat is the first sign of life and a critical milestone in pregnancy. Usually, a fetal heartbeat becomes detectable between the sixth and seventh week of gestation.
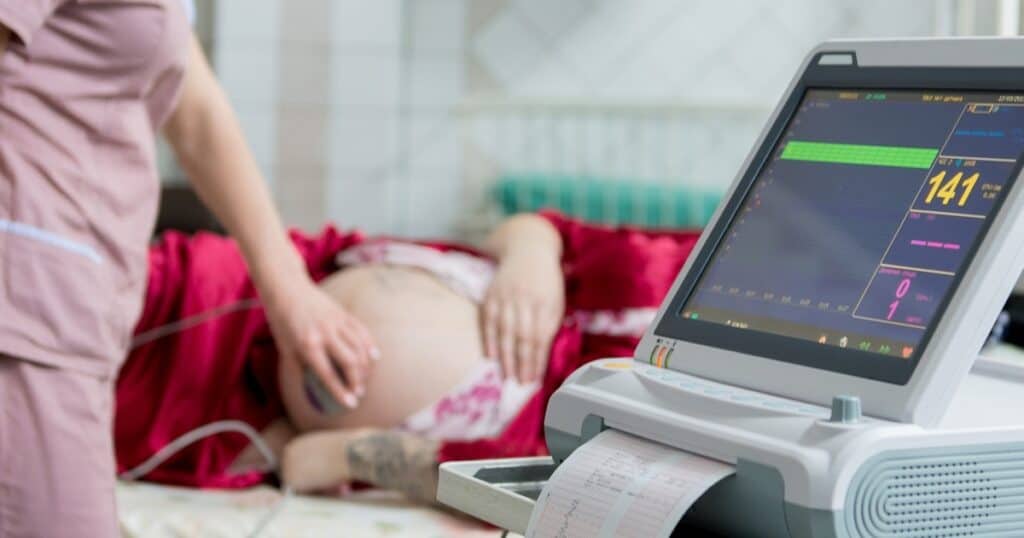
Healthcare providers use various tools and techniques to monitor the fetal heartbeat and ensure the health of the developing baby.
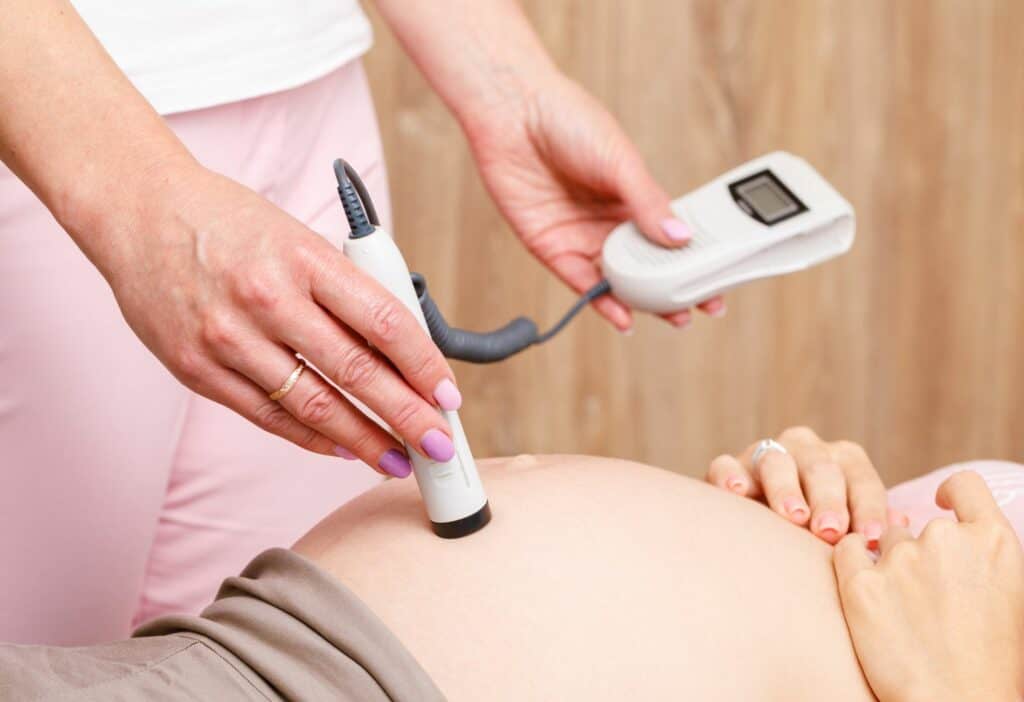
A commonly-used method to detect a fetal heartbeat is the doppler ultrasound. This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to create images of the fetus. The doppler ultrasound can be performed either as an abdominal ultrasound or a transvaginal ultrasound.
An abdominal ultrasound involves placing a small device on the mother’s abdomen to transmit sound waves, while a transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting a probe into the vagina to obtain clearer and more detailed images.
Another tool used for monitoring fetal heart rate is the fetal doppler or fetal heart monitor. This handheld device allows healthcare providers to listen to the baby’s heartbeat as it pumps blood.
This can be especially helpful during prenatal check-ups and labor. The handheld doppler simply needs to be placed on the mother’s abdomen to hear the heartbeat.
In some cases, a fetal heartbeat may not be detected in early ultrasounds. This could be due to several factors, such as:
- A miscalculation in the pregnancy’s gestational age
- The position of the fetus in the womb
- The mother’s body habitus, such as obesity or muscle mass
- The quality of the ultrasound equipment
In such situations, it is crucial not to panic, as the heartbeat may become more detectable later in the pregnancy.
Sometimes, a fetal heartbeat may appear to disappear and reappear, causing anxiety for expectant parents. This can occur when the fetus moves constantly or changes position, making it challenging for the doppler or ultrasound to pick up the signal accurately.
Factors like excessive maternal movement or improper use of the equipment can also contribute to this phenomenon.
In summary, understanding and accurately monitoring the fetal heartbeat is essential for the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Healthcare providers use tools like ultrasounds and dopplers to detect and track the fetal heart rate, ensuring a healthy pregnancy experience.
However, it is important to note that, occasionally, factors such as fetus position and equipment quality may temporarily affect the detectability of the heartbeat.
Possible Reasons for Fetal Heartbeat Disappearing
There could be a variety of reasons behind the disappearance of a fetal heartbeat. One possible reason is miscarriage. A miscarriage occurs when the pregnancy ends before the 20th week, and it may happen due to chromosomal abnormalities, infections, low progesterone, or chronic health conditions.
When this occurs, the heartbeat might disappear due to the fetus no longer developing.
Human error is another factor that may contribute to the seemingly absent heartbeat. During an ultrasound, the technician’s skill level, position of the fetus, or equipment limitations can lead to a missed or undetectable heartbeat.
In these instances, the heartbeat may eventually reappear when the conditions are more favorable for detection.
There are cases where a missed miscarriage might be the cause. A missed miscarriage occurs when the fetus has died but remains in the uterus without being expelled, resulting in the absence of a heartbeat. This type of miscarriage is often discovered during a routine prenatal appointment.
Umbilical cord complications could also hinder the detection of the fetal heartbeat. A cord twist or compression could lead to fluctuations in the heartbeat, causing it to disappear and reappear. The condition is usually temporary, and the heartbeat typically stabilizes in due time.
Infections during pregnancy might lead to complications, including the disappearance of the fetal heartbeat. Some infections, such as listeria or syphilis, can directly affect the fetus and potentially result in stillbirth or other serious problems.
Ectopic pregnancy is another potential reason for the absence of a detectable fetal heartbeat. This occurs when the fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes.
An ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally, and the lack of proper development can make detecting a heartbeat near impossible.
Thrombophilia, a condition that leads to abnormal blood clotting, may also play a role in the disappearance of a fetal heartbeat. This condition can lead to fetal growth restriction or placental abruption, both of which can affect the fetal heartbeat.
It is essential for pregnant individuals to monitor their symptoms and inform their healthcare provider of any changes or concerns. Regular prenatal appointments can help detect and address any issues early on, ensuring the best possible care for both the individual and the developing fetus.
Phenomenon of Fetal Heartbeat Reappearing
The phenomenon of a fetal heartbeat disappearing and then reappearing has raised questions and concerns among expecting parents. For medical professionals, understanding this occurrence can provide reassurance and guidance to those experiencing it.
During pregnancy, the fetus relies on the umbilical cord for oxygen and blood supply. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta, ensuring proper development. At certain points in gestational age, the fetus’s heartbeat might not be clearly detected using dopplers or ultrasound machines.
This temporary disappearance and reappearance are typically no cause for alarm but warrant further investigation.
In the initial weeks of pregnancy, it can be challenging to detect the fetal heartbeat due to the small size and early developmental stage of the fetus. As the gestational age progresses, the heartbeat should become more consistent and easier to identify.
It is important to note that estimating the gestational age based on dates can sometimes be inaccurate, leading to heartbeat detection at different stages than expected.
Fetal heartbeat detection can be influenced by various factors, such as the position of the fetus, the mother’s body composition, and the equipment used. In the second trimester, when the baby’s heartbeat is usually more developed and easier to locate, a temporary disappearance might still occur.
Often, the cause lies in a change in the fetus’s position or issues with the equipment, such as limited sensitivity of the dopplers or ultrasound device.
When a fetal heartbeat disappearance is noted, healthcare providers may recommend a follow-up appointment or a second opinion to confirm the findings. A Supplementary test, like a detailed ultrasound or a different doppler device, can help assess the situation more accurately.
In some cases, healthcare professionals might investigate the potential role of factors like progesterone levels in the temporary absence of the heartbeat.
In summary, the phenomenon of a fetal heartbeat disappearing and reappearing is not uncommon during pregnancy. Most often, it is due to the fetus’s developmental stage, equipment limitations, or the inability to accurately determine gestational age.
A second opinion or additional testing can provide reassurance to expecting parents, and healthcare professionals can help guide them through this process with a confident, knowledgeable, neutral, and clear approach.
Medical Procedures and Interventions
Doctors commonly utilize ultrasound technology to monitor fetal health during pregnancy. Two types of ultrasounds, doppler and transvaginal ultrasound, are typically used to assess the fetal heartbeat.
These non-invasive procedures allow medical professionals to visualize the embryo and detect its heartbeat.
Doppler ultrasound is a specialized form of ultrasound that measures the blood flow in the fetus’s heart and blood vessels. This technology can help identify any potential abnormalities or complications.
In some cases, a fetal heartbeat might not be detected with a doppler ultrasound, prompting the need for further investigation.
When a doctor suspects an issue, they may opt for a transvaginal ultrasound. This procedure differs from a standard ultrasound because it uses a probe placed inside the vagina to capture more detailed images of the embryo.
The transvaginal ultrasound provides a closer inspection of the fetus and can sometimes detect a previously unnoticed heartbeat.
The use of a fetal doppler is another option for monitoring the fetal heartbeat. A fetal doppler is a handheld device that emits ultrasound waves to listen to the baby’s heartbeat, and it is usually employed in later stages of pregnancy.
However, it is important to note that over-the-counter fetal doppler devices are not a substitute for professional medical care.
Upon the disappearance or undetection of a fetal heartbeat, the doctor may advise waiting for a few weeks to carry out another ultrasound. It could be that the embryo is still too small and not yet visible.
Getting a second opinion is also a viable option, as different medical professionals might have varying interpretations of ultrasound results.
In some cases, a doctor may recommend a D&C procedure (dilation and curettage) if they suspect a miscarriage. However, it is essential to seek advice from a medical professional before deciding on any intervention.
In conclusion, various medical procedures and interventions, like ultrasound during pregnancy, are available for detecting and monitoring the fetal heartbeat. It is crucial to consult with a medical professional at each stage to ensure accurate readings and appropriate care throughout pregnancy.
Role of Mother’s Body
During pregnancy, various factors related to the mother’s body can affect the detection of fetal heartbeat. One such factor is the position of the uterus. A tilted uterus can make it harder for a healthcare provider to find the heartbeat using a Doppler or ultrasound, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.
This is because the position of the tilted uterus can cause the baby to be at a more awkward angle for detecting heartbeats.
Additionally, a mother’s body weight plays a role in the detection of fetal heartbeat. In an overweight or plus-sized mother, there may be more fatty tissue between the baby and the surface of the skin, making it difficult to detect the heartbeat using an ultrasound or Doppler.
This tissue can affect both the clarity and accuracy of the heartbeat detection.
The development of the placenta is also crucial in determining the fetal heartbeat detection. If the mother has an anterior placenta, meaning it is attached to the front of the uterus, it may act as a barrier between the baby and the ultrasonic waves emitted during a Doppler examination.
Due to its positioning, the anterior placenta can interfere with the clarity of the heartbeat detection, which might create a temporary perception of the absence of a heartbeat.
Furthermore, the levels of progesterone, a hormone responsible for maintaining the pregnancy, can impact the visibility of the fetal heartbeat. If the mother has irregular ovulation patterns, it could lead to lower progesterone levels, affecting the detection of the heartbeat, and increasing the risk of blood clots forming in the uterus.
In summary, the role of a mother’s body, including factors such as the position and weight of the uterus, the development of the placenta, and her hormone levels, can influence the detection of a fetal heartbeat. It is essential to take these factors into account when trying to understand variations in heartbeat visibility during pregnancy.
Conclusion and Support
In the journey of pregnancy, many expectant parents may worry about the possibility of a disappearing and reappearing fetal heartbeat. It is important to seek the guidance of a medical professional or doctor when concerns arise.
They have the expertise necessary to evaluate the situation and can take the appropriate measures to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
In some instances, a fetal heartbeat may be difficult to detect initially, but may be found later on. Factors such as the position of the fetus, the mother’s body composition, or simply the early gestational age could make the heartbeat initially undetectable.
In these cases, it is essential to stay in close contact with your medical professional and follow their advice for monitoring the pregnancy.
If the heartbeat detection remains a concern, seeking a second opinion from another qualified professional can provide added reassurance. It is crucial to have proof of life for the fetus, as it signifies a viable pregnancy and can alleviate concerns about a disappearing and reappearing heartbeat.
It is equally important to have a strong support system in place, composed of loved ones, friends, and other expecting parents. Sharing one’s experiences and fears can provide not only emotional comfort, but also practical advice based on others’ experiences.
Online forums and local support groups can also be helpful resources for exchanging information and ideas.
In summary, while the concern of a disappearing and reappearing fetal heartbeat can cause anxiety for expectant parents, relying on the advice of medical professionals, being proactive in seeking information, and having a strong support network can help maintain a clear mind and confidence throughout the pregnancy journey.
You might want to check out an interesting post: Can You Go Into Labor While Sleeping
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a fetus stop growing and then start again?
It is generally not possible for a fetus to stop growing and then start again. If there is a temporary halt in the growth, it could be due to inaccurate measurements or the differing growth rates of various body parts. However, consistent growth is important and any concerns should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
No heartbeat at 10 weeks, could baby still be alive?
In some cases, a heartbeat may not be detected at 10 weeks due to factors such as the baby’s position or the type of ultrasound equipment used. It is essential to consult with a medical professional to determine any potential issues and consider a follow-up ultrasound if needed.
Can an ultrasound be wrong about no heartbeat at 9 weeks?
Ultrasound technology is highly accurate, but there is a possibility of an error in detecting a heartbeat at 9 weeks. Factors such as the position of the baby, the quality of the equipment, or the experience of the technician can affect the results.
It is crucial to discuss ultrasound findings with a healthcare provider and determine if a follow-up scan is necessary.
What are the symptoms of fetal heartbeat stopping?
Symptoms of a fetal heartbeat stopping might include a decrease in pregnancy symptoms, bleeding, cramping, or passing tissue. However, some women may not experience any apparent symptoms.
It is essential to contact a healthcare provider if any signs of concern arise or if there is a sudden change in pregnancy symptoms.
How common is a missed miscarriage after seeing a heartbeat?
A missed miscarriage, when the fetus has stopped developing but is not spontaneously expelled, is relatively rare after seeing a heartbeat. The majority of pregnancies continue successfully after a heartbeat has been confirmed.
However, the risk may still be present, so it is crucial to maintain regular contact with a healthcare provider throughout pregnancy.
Can an ultrasound technician be incorrect about no heartbeat?
An ultrasound technician might be incorrect about the absence of a heartbeat due to factors such as the baby’s position, the equipment used, or their level of experience. It is essential to discuss any concerns regarding the results with a healthcare provider and consider the possibility of a follow-up ultrasound if deemed necessary.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.