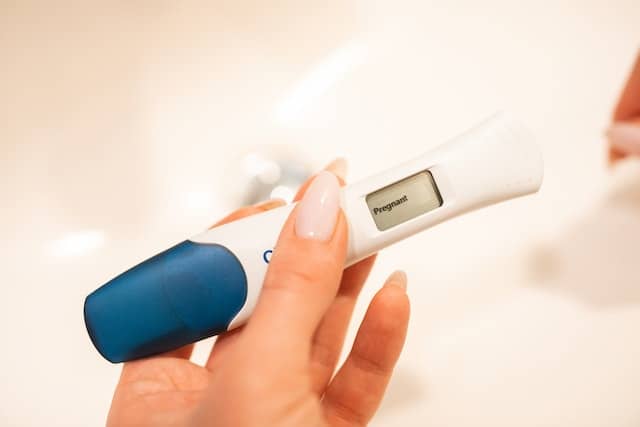
Ovulation tests, commonly known as ovulation predictor kits (OPKs), are widely used by women to identify their fertile window – the time during their menstrual cycle when they have the highest chance of conceiving.
These tests measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) in a woman’s urine, which usually surges right before ovulation. However, many women also wonder if these tests can be used to detect early pregnancy.
Pregnancy occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg during ovulation. In the early stages of pregnancy, a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is released, which is essential for the successful implantation and development of a fertilized egg.
Pregnancy tests are specifically designed to detect the presence of hCG in a woman’s urine or blood. It is important to understand the difference between the role of hormones in ovulation and pregnancy to determine if ovulation tests can indeed detect early pregnancy.
Key Takeaways
- Ovulation tests measure LH levels to identify a woman’s fertile window
- Pregnancy tests detect the presence of hCG hormone to confirm pregnancy
- Understanding the difference between hormones in ovulation and pregnancy is essential
Understanding Ovulation and Pregnancy
Ovulation is a crucial part of the menstrual cycle, as it’s the time when a woman’s ovary releases a mature egg. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm.
The menstrual cycle usually lasts about 28 days, but it can vary from person to person.
During the first half of the cycle, levels of estrogen rise, thickening the lining of the uterus to prepare for a potential pregnancy. Around the middle of the cycle, a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation.
If the egg is not fertilized within about 24 hours after ovulation, it will disintegrate, and the woman’s hormone levels will decline. This leads to the shedding of the lining of the uterus, known as menstruation.
Conception occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg during the window of fertility, which typically lasts about five days before ovulation and one day after. It’s essential to understand that conception is different from pregnancy.
Pregnancy is only confirmed when the fertilized egg successfully implants itself into the lining of the uterus.
While an ovulation test can predict the most fertile days in a woman’s cycle, it’s essential to know that these tests are not designed to detect pregnancy. Ovulation tests work by measuring the levels of LH in urine, which surge about 24 to 48 hours before ovulation.
A positive ovulation test simply means the LH surge is detected, indicating that ovulation is likely to occur soon.
In contrast, pregnancy tests measure the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine. This hormone is only produced after successful implantation of a fertilized egg.
It’s important to remember that relying on ovulation tests to detect early pregnancy could lead to false conclusions, as elevated LH levels do not guarantee that a woman is pregnant.
In summary, ovulation tests are helpful for predicting fertility, but they are not intended for detecting early pregnancy. To confirm pregnancy, using a pregnancy test specifically designed to measure hCG levels is the most accurate and reliable method.
Role of Hormones
Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and ovulation process. Produced in the brain’s pituitary gland, it stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles. These follicles, in turn, produce estrogen.
As estrogen levels rise, a tipping point is reached, leading to a rapid increase in LH levels, known as the LH surge. The surge causes the mature follicle to release an egg, marking the beginning of the ovulation process.
Ovulation tests detect the presence of LH in urine. When LH levels surge, it indicates that the woman is about to ovulate or is currently ovulating.
Keeping track of this hormonal change can help women identify their fertile window, increasing their chances of conceiving.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) is another hormone involved in the reproductive process. After fertilization, the embryo implants itself into the uterus and starts producing hCG.
The placenta, responsible for supplying nutrients to the developing fetus, also releases hCG during pregnancy.
It is important to note that hCG and LH share a similar molecular structure. As a result, ovulation tests may detect hCG in some cases, causing a false positive result.
However, this scenario is relatively rare, and ovulation tests are not specifically designed to detect early pregnancy.
To reliably confirm a pregnancy, a pregnancy test that specifically measures hCG levels should be used. These tests are more sensitive to hCG and can provide accurate results as early as a few days before a missed period.
Monitoring LH and hCG levels can provide valuable information about a woman’s fertility status and the presence of a pregnancy. However, to ensure accurate results, it is essential to use the appropriate test for each purpose – an ovulation test for tracking fertility and a pregnancy test for confirming pregnancy.
Ovulation Testing
Ovulation testing can be helpful for individuals trying to conceive or track their menstrual cycle. These tests identify important changes in hormone levels that indicate the most fertile period for conception.
There are two main types of ovulation tests: ovulation test strips and ovulation predictor kits.
Ovulation Test Strips
Ovulation test strips are an affordable and simple way to detect ovulation. They work by measuring the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge that occurs approximately 24 to 48 hours before ovulation. To use an ovulation test strip, it must be immersed in a urine sample for a specified period of time.
Then, the strip will display lines or symbols to indicate the result. Typically, a positive result indicates that ovulation will occur within one to two days.
Some key features of ovulation test strips include:
- Affordable: These strips are generally less expensive than ovulation predictor kits.
- Simple: The process to use an ovulation test strip is straightforward and quick.
- Accessible: They are widely available at pharmacies and online retailers.
Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are more advanced than test strips and usually provide a digital readout of the results. Like test strips, OPKs measure the LH surge that precedes ovulation.
However, some kits may also detect the presence of another fertility hormone called estrogen. These kits can give more precise information regarding the most fertile days of the cycle.
Some benefits of using ovulation predictor kits include:
- Accurate: OPKs provide a precise result with digital readings, reducing the chance of misinterpretation.
- Convenience: Unlike test strips, OPKs often come with additional features, such as tracking apps or personalized fertility advice.
- Comprehensive: Some kits measure both LH and estrogen levels to provide a more detailed picture of fertility.
It is important to note that ovulation tests are designed to predict ovulation, not confirm it. They are not intended to be used as a method of contraception or to detect early pregnancy.
For early pregnancy detection, a different test called a pregnancy test should be used, which measures the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy tests come in various forms, but they generally rely on detecting the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy. There are two common types of pregnancy tests: home pregnancy tests and blood pregnancy tests.
Both methods can help individuals determine if they are pregnant, but they differ in terms of accuracy and convenience.
Home Pregnancy Tests
Home pregnancy tests are widely accessible over-the-counter options that measure hCG levels in urine. These tests are popular due to their ease of use and quick results, often available within minutes.
To use a home pregnancy test, one should follow the instructions provided on the packaging, which generally involve collecting a urine sample or dipping the test strip in urine.
The accuracy of home pregnancy tests depends on various factors, including the timing of the test, hCG levels in the urine, and the specific test’s sensitivity. Early pregnancy tests can detect lower levels of hCG, allowing women to test sooner than standard home pregnancy tests.
However, hCG levels increase rapidly during the first few weeks of pregnancy, so testing too early may result in a false-negative result. It is generally recommended to wait until the first day of a missed period to take a home pregnancy test for the most accurate results.
Blood Pregnancy Tests
Blood pregnancy tests are conducted by healthcare professionals and can detect pregnancy earlier than home pregnancy tests. These tests measure hCG levels in blood and can provide a more accurate assessment of pregnancy.
There are two types of blood pregnancy tests: qualitative and quantitative.
- Qualitative tests confirm the presence of hCG in the blood, providing a simple “yes” or “no” result.
- Quantitative tests measure the specific amount of hCG in the blood, providing more detailed information about the progression of the pregnancy.
Blood tests can detect pregnancy as early as one week after conception, while home pregnancy tests are typically accurate around two weeks after conception. While blood tests can provide earlier and more precise results, they require a visit to a healthcare provider and may take longer to receive results compared to home pregnancy tests.
In summary, both home pregnancy tests and blood pregnancy tests can detect early pregnancy by measuring hCG levels. The choice between the two depends on factors such as convenience, timing, and required accuracy.
It is essential to follow instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns or uncertainties regarding pregnancy tests.
Accuracy and Result Interpretation
Negative Result
A negative ovulation test result indicates that there is no detectable luteinizing hormone (LH) surge, meaning it’s unlikely that ovulation will occur soon. In this case, the control line will be darker than the test line.
However, a negative result does not necessarily mean that the person is not pregnant, as ovulation tests are designed to detect LH surge, not human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone, which is produced during pregnancy.
Positive Result
A positive ovulation test result is when the test line is as dark or darker than the control line. This means that an LH surge is detected, and ovulation is likely to occur within the next 24-48 hours.
But, keep in mind that a positive ovulation test is not a confirmation of pregnancy since it detects LH, not hCG.
False Negative Result
False negative results can occur if the test is taken too early or too late in the cycle, or the urine sample is too diluted. It’s important to account for these factors when interpreting accuracy.
To minimize the chances of a false negative result:
- Test at a consistent time each day
- Reduce fluid intake for a couple of hours before taking the test
- Use an ovulation test with high sensitivity to better detect an LH surge.
False Positive Result
False positive results can occur if the person is taking fertility medications that contain LH or when interpreting results after the recommended time. Some medical conditions, like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), can cause elevated LH levels throughout the cycle, potentially causing false positive results.
To ensure accuracy, it’s important to follow the instructions provided with the ovulation test, and keep in mind that these tests do not guarantee the detection of pregnancy.
Detecting Early Pregnancy
Detecting early pregnancy can be challenging, as the signs and symptoms vary among individuals. However, certain hormones and tests can provide valuable information about the presence of a pregnancy.
Ovulation tests and pregnancy tests have some similarities but are primarily designed to serve different purposes. Understanding these tests’ purposes can help determine their effectiveness in early pregnancy detection.
Ovulation tests detect the luteinizing hormone (LH), which surges before ovulation. The fertility window is the time during a woman’s menstrual cycle when she has the highest chance of conceiving.
It usually lasts for a few days around the time of ovulation. Using ovulation tests can help identify this period and increase the chances of conception.
On the other hand, early detection pregnancy tests measure the presence of the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), commonly known as the pregnancy hormone. This hormone is produced by the developing placenta after implantation, which occurs a few days after conception.
A higher hCG level generally indicates pregnancy, but it’s important to note that the hormone level can vary among pregnant individuals.
While ovulation tests primarily detect LH, they might also show positive results when hCG is present in the body. This is because both hormones have similar chemical structures, and ovulation tests might be unable to differentiate them.
However, this approach might produce false-positive results and is not a reliable method for detecting early pregnancy compared to using a proper pregnancy test.
When to take a pregnancy test depends on the type of test being used. Blood tests can detect hCG earlier than urine tests, with some even detecting it within a week after ovulation. However, these tests require a visit to a healthcare professional.
Home pregnancy tests are more convenient and can detect hCG within a few days of a missed period. To increase accuracy, it’s recommended to wait at least a week after a missed period to take a urine pregnancy test.
In summary, ovulation tests are primarily designed to detect LH and identify the fertility window, while pregnancy tests measure the presence of hCG to confirm pregnancy. Although ovulation tests might show a positive result during early pregnancy, they are not a reliable method for confirming a pregnancy.
It’s best to use a proper pregnancy test at the appropriate time for accurate and reliable results.
Fertility Challenges and Treatments
PCOS and Ovulation Testing
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects many women in their reproductive years. It can cause irregular periods and make it harder to get pregnant. Women with PCOS may have difficulty determining their fertile window, which is the optimum time to try for a baby.
This is because their cycle length can be unpredictable, and ovulation may not occur consistently.
Ovulation testing can help women with PCOS identify their fertile window. These tests detect a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that typically occurs 24 to 48 hours before ovulation.
It is important to note, however, that ovulation tests may not be as accurate for women with PCOS, as they can have elevated LH levels throughout their cycle.
Fertility Treatments
For couples who have been trying to conceive (TTC) without success, fertility treatments may be helpful. There are several options available, depending on the individual’s specific fertility challenges:
- Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid): A popular medication that stimulates ovulation by increasing the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This may help women with PCOS, as well as those with irregular periods and unexplained infertility.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): A procedure that involves placing sperm directly into the uterus, bypassing the cervix. This can increase the chances of the sperm reaching the egg and may be helpful for couples with mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or mild endometriosis.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): A more invasive and expensive treatment option, IVF involves collecting eggs and sperm, fertilizing them in a lab, and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. This can be helpful for couples with more complex fertility challenges, such as blocked fallopian tubes, severe male factor infertility, or poor egg quality.
Regardless of the treatment option chosen, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, tracking one’s cycle, and seeking appropriate medical support can increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
Additionally, understanding the impact of conditions like PCOS and utilizing ovulation tests can help women more accurately identify their fertility window, increasing their chances of conception.
The Role of Sex in Conception
Sex plays a crucial role in conception as it allows the sperm to enter the woman’s reproductive system, beginning its journey toward the egg. During sexual intercourse, ejaculated sperm enters the vagina, swims through the cervix, and makes its way into the uterus.
Within the uterus, sperm encounters yet another obstacle, the fallopian tubes. These tubes connect the uterus to the ovaries, where eggs are released during ovulation.
Sperm must navigate through one of these tubes in order to reach an egg, which may be waiting in the fallopian tube after ovulation.
While millions of sperm are released during ejaculation, only a small percentage will successfully reach the fallopian tube. Here, they will encounter the released egg.
For conception to occur, a single sperm must penetrate the outer layers of the egg, ultimately resulting in a fertilized egg.
Once fertilization takes place, the fertilized egg gradually descends through the fallopian tube and into the uterus. During this time, the fertilized egg undergoes multiple cell divisions, forming a blastocyst.
Upon reaching the uterus, the blastocyst will implant itself into the uterine lining, signifying the beginning of a pregnancy.
Understanding the role of sex in conception, as well as the journey of sperm and the process of fertilization, can provide valuable insight for couples who are trying to conceive.
By timing intercourse around the woman’s ovulation, the likelihood of sperm meeting egg is increased, ultimately improving the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
Monitoring Physical Symptoms
Monitoring physical symptoms is one important step to help determine the possibility of early pregnancy. While an ovulation test may not be the go-to method to detect early pregnancy, keeping track of bodily changes can provide valuable information.
One key sign of pregnancy is a missed period. If a woman’s menstrual cycle is regular and she suddenly misses her expected period, it may be a potential indicator of pregnancy. However, irregular cycles or stress might also contribute to a missed period, so it is essential to consider other symptoms as well.
Bloating is another common physical symptom experienced during early pregnancy. This occurs due to hormonal fluctuations, which cause the body to retain more water and gas.
Bloating can be quite similar to the sensations experienced before a menstrual period, but if it persists or intensifies, it could be a sign of pregnancy.
The presence and consistency of cervical mucus can also provide insight into pregnancy. During the menstrual cycle, the amount and texture of cervical mucus change. In early pregnancy, there is often an increase in the production of cervical mucus, and it becomes thicker in consistency.
This happens as the body’s way of creating a protective barrier for the growing embryo. Monitoring the quantity and appearance of cervical mucus can help identify early pregnancy, alongside other symptoms.
In conclusion, paying attention to physical symptoms like missed periods, bloating, and changes in cervical mucus may help in detecting early pregnancy. Although an ovulation test is not designed to detect pregnancy, monitoring physical symptoms can give some valuable clues.
Nonetheless, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate and reliable confirmation of pregnancy.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
When trying to detect early pregnancy, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for accurate information and guidance. They can provide the most reliable information on the methods and tests available for determining early pregnancy and ovulation.
A doctor may suggest various types of pregnancy tests, such as blood tests and urine tests, to confirm the pregnancy. These tests differ in their sensitivity and the time at which they can detect pregnancy hormones, hCG.
Blood tests can detect pregnancy earlier than urine tests, usually within 7-12 days after conception. On the other hand, urine tests, like home pregnancy tests, are generally accurate around one week after a missed period.
Healthcare providers can also discuss birth control options and their effectiveness in preventing pregnancy. There are several types of birth control methods, each with a unique mode of action and effectiveness rate.
Consulting a doctor can help you make an informed decision based on your medical history, personal preferences, and lifestyle factors.
While ovulation tests are incredibly useful for predicting when ovulation will occur, they should not be relied upon as a method for detecting early pregnancy. Ovulation tests detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that precedes ovulation, which differs from the pregnancy hormone hCG.
Although LH and hCG have similar molecular structures, an ovulation test cannot specifically detect hCG and, therefore, cannot confirm pregnancy.
In conclusion, to obtain the most accurate and reliable information about early pregnancy detection and ovulation, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider.
They can recommend the best tests and methods based on individual needs, discuss birth control options, and step in promptly to provide appropriate guidance and support.
Final Thoughts
Ovulation tests play an important role in helping people understand their menstrual cycles and pinpoint their fertile windows. These tests use advanced technology to detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) in a person’s body, which occurs 12 to 36 hours before ovulation.
While ovulation tests are designed specifically to track fertility, they are not intended as early pregnancy detection tools.
However, in some cases, they may show a positive result due to the similarities in the molecular structures of LH and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone that increases during early pregnancy.
It is important to remember that using an ovulation test for pregnancy detection is not a reliable method and may lead to false positives or negatives. This is because several factors, such as irregular menstrual cycles, can influence the accuracy of ovulation tests.
To confirm pregnancy, it is recommended to use a home pregnancy test designed specifically to detect hCG or consult a healthcare professional.
It is important for individuals trying to conceive or track their menstrual cycles to use the appropriate testing methods and technology tailored to their specific needs. This will provide the most accurate and helpful information for understanding fertility and managing reproductive health.
Ultimately, while ovulation tests can be useful tools for tracking fertility, they should not be relied upon as early pregnancy detectors. Instead, utilize pregnancy tests and professional advice to confirm and manage a healthy pregnancy journey.
Related posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an ovulation test indicate pregnancy?
An ovulation test is designed to detect the presence of the hormone luteinizing hormone (LH) in a woman’s urine. While the purpose of an ovulation test is to identify the surge in LH levels that precedes ovulation, it is not specifically intended to detect pregnancy.
That said, it is possible that an ovulation test may show a positive result in the early stages of pregnancy due to an overlap in hormones.
Will a positive ovulation test mean I am pregnant?
A positive ovulation test indicates a high level of LH in the body, suggesting that ovulation is likely to occur soon. This does not directly mean that you are pregnant. To confirm pregnancy, a pregnancy test, which detects the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), should be used.
Is it possible to use an ovulation test for pregnancy detection?
An ovulation test is not designed for pregnancy detection and may not be reliable for this purpose. However, in some cases, it might show a positive result during early pregnancy due to the similar molecular structures of hCG and LH.
To ensure accurate detection of pregnancy, use a pregnancy test that specifically targets the hCG hormone.
How does LH surge relate to early pregnancy?
The LH surge is a spike in luteinizing hormone levels, signaling that ovulation is about to occur. If conception takes place during this time, the fertilized egg will implant itself in the uterus, leading to early pregnancy.
As LH levels naturally decrease after ovulation, a persistently high LH level could indicate that hCG is also present, possibly due to pregnancy.
Why is my pregnancy test negative but ovulation test positive?
A negative pregnancy test coupled with a positive ovulation test could be due to several reasons. First, it might be an indication that ovulation is imminent but pregnancy has not yet occurred. Second, hCG levels could still be too low for detection by a pregnancy test if the pregnancy is in its very early stages.
Finally, a false negative pregnancy test result is possible, so it is recommended to repeat the test after a few days if you still suspect pregnancy.
Does a faint line on an ovulation test suggest pregnancy?
A faint line on an ovulation test usually indicates low levels of LH, meaning that ovulation is not imminent. This result is not a reliable indicator of pregnancy, as the test is not designed to detect hCG. To confirm pregnancy, use a pregnancy test specifically designed for detecting hCG levels.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.