Canker sores are painful, small ulcers that appear inside the mouth, on the gums, cheeks, tongue, or throat. They can be a nuisance to anyone, but for pregnant women, they can be even more challenging.
Canker sores and pregnancy are a common combination, and many women experience them during their pregnancy.
While the exact cause of canker sores is unknown, there are several factors that can trigger them. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, stress, and nutritional deficiencies are some of the most common causes.
Pregnant women are already dealing with a lot of changes in their bodies, and canker sores can add to the discomfort.
Key Takeaways
- Canker sores are small ulcers that can appear inside the mouth, gums, cheeks, tongue, or throat.
- Pregnant women are more likely to experience canker sores due to hormonal changes, stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding common triggers can help prevent and manage canker sores during pregnancy.
Understanding Canker Sores
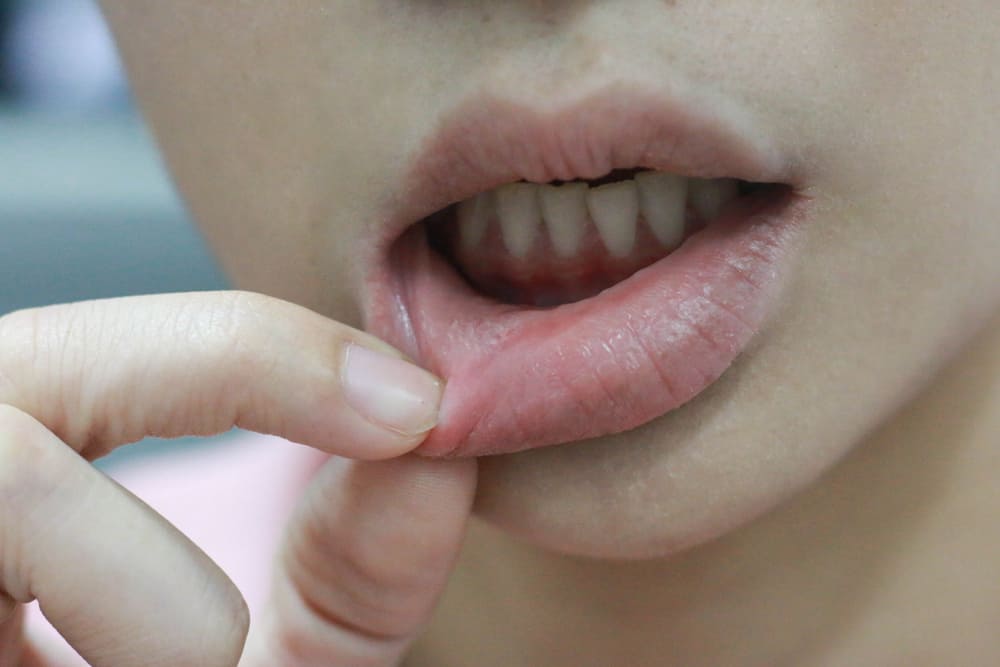
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are small, painful ulcers that appear inside the mouth. They can occur on the tongue, gums, inside of the cheeks, and lips.
Canker sores are not contagious and usually heal on their own within one to two weeks.
There are two types of canker sores: minor canker sores and major canker sores. Minor canker sores are the most common and usually less than 1cm in diameter.
They typically heal on their own within a week or two. Major canker sores are less common and can be larger than 1cm in diameter. They may take several weeks to heal and can leave a scar.
The exact cause of canker sores is unknown, but they may be triggered by stress, injury to the mouth, certain foods, hormonal changes, or a weakened immune system. Women may be more prone to canker sores during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
Canker sores can be painful and uncomfortable, but there are several ways to alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, topical ointments, and mouthwashes can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Avoiding spicy or acidic foods and using a soft-bristled toothbrush can also help prevent further irritation.
If canker sores persist or are accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or difficulty swallowing, it is important to seek medical attention. In some cases, canker sores may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
Causes of Canker Sores
Canker sores are small, painful ulcers that appear in the mouth. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, injury, and bacteria.
Stress is a common trigger for canker sores. When a person is under stress, their immune system is weakened, making them more susceptible to infections and other health problems. Emotional stress, such as anxiety or depression, can also lead to canker sores.
Injury or trauma to the mouth can also cause canker sores. This can include accidentally biting the inside of the cheek or lip, or brushing too hard with a toothbrush. Canker sores can also be caused by dental work, such as braces or dentures.
Bacteria can also play a role in the development of canker sores. Some types of bacteria can cause infections in the mouth, leading to the formation of canker sores.
Overall, the exact cause of canker sores is not fully understood. However, by avoiding triggers such as stress and injury, and maintaining good oral hygiene, it is possible to reduce the frequency and severity of canker sores.
Symptoms of Canker Sores
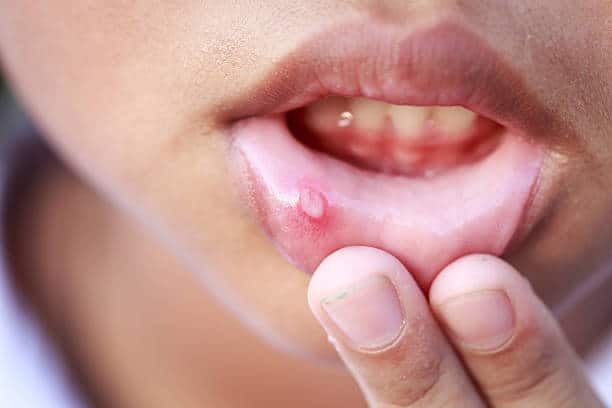
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are small, painful lesions that develop on the soft tissues of the mouth, including the inside of the lips, cheeks, and under the tongue. These sores can also appear on the gums and roof of the mouth.
Canker sores typically have a round or oval shape and are red or pink in color. They can also be white, yellow, or gray and may have a red border. The sores can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
The most common symptom of a canker sore is pain. The sore may also cause a burning sensation or tingling in the affected area. Eating, drinking, and brushing teeth can all exacerbate the pain.
In addition to pain, canker sores can also cause other symptoms, including:
- Swelling and inflammation of the affected area
- Difficulty eating or speaking due to pain
- Fever in severe cases
- A general feeling of malaise
It is important to note that canker sores are not contagious and are not caused by a virus or bacteria. They are thought to be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods.
If you develop a canker sore that is unusually large or lasts for more than two weeks, you should see a healthcare provider. They may recommend a topical ointment or prescribe an oral medication to help alleviate the symptoms.
Canker Sores and Pregnancy
Canker sores are small, painful ulcers that can develop inside the mouth, on the tongue, or on the gums. While they are not contagious, they can be quite uncomfortable.
Pregnant women are more likely to develop canker sores due to hormonal changes in their bodies.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause an increase in progesterone levels. This increase in progesterone can lead to changes in the immune system, making it more likely for a woman to develop canker sores.
Additionally, women may experience canker sores during menstruation, which can also be attributed to hormonal changes.
It is important for pregnant women to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent the development of canker sores. Brushing and flossing regularly can help to reduce the risk of developing canker sores.
Additionally, avoiding spicy or acidic foods can also be helpful in preventing canker sores.
If a pregnant woman does develop a canker sore, there are several over-the-counter treatments that can be used to help alleviate the pain and discomfort. These treatments include topical ointments, mouthwashes, and pain relievers.
It is important for pregnant women to speak with their healthcare provider if they experience frequent or severe canker sores. In some cases, canker sores may be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires medical attention.
Nutrition and Canker Sores
Nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining good oral health. Adequate intake of essential nutrients can help prevent and manage canker sores during pregnancy.
Here are some nutrients that pregnant women should include in their diet to reduce the risk of canker sores:
1. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that helps in the healing of canker sores. Pregnant women should consume foods rich in zinc, such as oysters, beef, pork, chicken, beans, and nuts. Zinc supplements can also be taken under medical supervision.
2. Folic Acid
Folic acid, also known as folate, is essential for the healthy development of the fetus. It also helps prevent canker sores. Pregnant women should consume foods rich in folate, such as leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified cereals.
3. Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps in the absorption of calcium, which is essential for strong teeth and bones. Pregnant women should consume foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified milk. Vitamin D supplements can also be taken under medical supervision.
4. Iron
Iron is essential for the healthy development of the fetus. Pregnant women should consume foods rich in iron, such as lean red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and fortified cereals. Iron supplements can also be taken under medical supervision.
5. Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for the healthy development of the fetus and the nervous system. Pregnant women should consume foods rich in vitamin B12, such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Vitamin B12 supplements can also be taken under medical supervision.
6. Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are rich in essential vitamins and minerals that help maintain good oral health and prevent canker sores. Pregnant women should consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, such as berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables.
7. Nutritional Supplements
Nutritional supplements can be taken under medical supervision to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients during pregnancy. However, pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking any nutritional supplements to avoid any adverse effects.
8. Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can increase the risk of canker sores during pregnancy. Pregnant women should ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients through a balanced diet and supplements, if necessary.
In conclusion, pregnant women should consume a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients to prevent and manage canker sores during pregnancy. Adequate intake of zinc, folic acid, vitamin D, iron, vitamin B12, fruits, and vegetables can help maintain good oral health and prevent canker sores.
Nutritional supplements can also be taken under medical supervision to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
Oral Health Practices
Maintaining good oral health is crucial during pregnancy to prevent canker sores and other dental problems. Here are some oral health practices that pregnant women can follow:
- Brushing: Pregnant women should brush their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. They should use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently to avoid irritating their gums.
- Flossing: Flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and along the gum line. Pregnant women should use floss that is gentle on their gums.
- Tongue cleaning: Cleaning the tongue with a tongue scraper or a soft-bristled toothbrush can help remove bacteria that cause bad breath.
- Mouthwash: Using an alcohol-free mouthwash can help kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Visiting the dentist: Pregnant women should continue to see their dentist for regular checkups and cleanings. They should inform their dentist that they are pregnant and avoid X-rays unless absolutely necessary.
- Lip care: Keeping lips moisturized with lip balm can help prevent dryness and cracking.
- Avoiding sugary foods and drinks: Consuming sugary foods and drinks can increase the risk of tooth decay and canker sores. Pregnant women should choose healthier options like fruits and vegetables.
By following these oral health practices, pregnant women can reduce their risk of developing canker sores and other dental problems.
Common Irritants and Triggers

Canker sores are painful and uncomfortable lesions that can occur in the mouth. For pregnant women, canker sores can be an added discomfort to their already changing bodies. While the exact cause of canker sores is unknown, there are several common irritants and triggers that can cause them to develop.
One of the most common irritants is spicy or acidic foods. These types of foods can cause irritation to the lining of the mouth and trigger the development of canker sores. Pregnant women should avoid these types of foods, or at least limit their consumption, to prevent the development of canker sores.
Food sensitivities can also be a trigger for canker sores. If a pregnant woman has a food sensitivity, consuming that food can cause an inflammatory response in the body, leading to the development of canker sores.
It is important for pregnant women to identify any food sensitivities they may have and avoid those foods to prevent the development of canker sores.
Other common irritants and triggers for canker sores include stress, hormonal changes, and trauma to the mouth. Pregnant women should take steps to manage their stress levels and avoid any trauma to the mouth to prevent the development of canker sores.
In summary, pregnant women should be aware of common irritants and triggers for canker sores, such as spicy or acidic foods, food sensitivities, stress, hormonal changes, and trauma to the mouth.
By avoiding or limiting exposure to these triggers, pregnant women can reduce their risk of developing canker sores and minimize any discomfort associated with them.
Treatment Methods
Canker sores during pregnancy can be quite painful and uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to help manage the symptoms.
One of the most effective ways to treat canker sores is to see a doctor or dentist. They can prescribe medications such as corticosteroids or antimicrobial mouth rinses that can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Another popular treatment method is to apply ice directly to the sore. This can help numb the area and reduce pain and swelling. It is important to wrap the ice in a cloth or towel to prevent damage to the surrounding tissue.
Over-the-counter creams and gels containing benzocaine or lidocaine can also be used to help alleviate pain. However, it is important to use these products as directed and not exceed the recommended dosage.
There are also several home remedies that can be used to treat canker sores. These include rinsing the mouth with salt water or baking soda, applying aloe vera gel, or using a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and water to clean the affected area.
It is important to note that some medications and home remedies may not be safe to use during pregnancy. It is always best to consult with a doctor or healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing canker sores during pregnancy can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help minimize the risk of developing them. Here are some tips to consider:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly can help prevent canker sores from forming. It is also important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid brushing too hard, which can irritate the gums and lead to canker sores.
- Manage Stress: Stress is a common trigger for canker sores. Pregnant women should try to manage their stress levels by practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Certain foods, such as citrus fruits, spicy foods, and acidic foods, can trigger canker sores. Pregnant women should try to avoid these foods or limit their consumption.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep the mouth hydrated and prevent canker sores from forming.
- Rest and Relaxation: Getting enough rest and relaxation is important for overall health and can help prevent canker sores.
- Avoid Trauma to Soft Tissue: Trauma to the soft tissue in the mouth, such as biting the inside of the cheek or lip, can lead to canker sores. Pregnant women should be careful when eating and chewing to avoid accidentally biting the soft tissue.
- Reduce Inflammation: Inflammation in the mouth can increase the risk of developing canker sores. Pregnant women should avoid using tobacco products and limit alcohol consumption to reduce inflammation.
By following these prevention strategies, pregnant women can reduce their risk of developing canker sores and maintain good oral health during pregnancy.
Other Related Conditions
Canker sores are not the only oral condition that can occur during pregnancy. Other related conditions include herpes and cold sores. Herpes is a viral infection that can cause sores on the mouth, lips, and genitals. Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus and usually appear on or around the lips.
It is important to note that herpes and cold sores are contagious and can be transmitted to the baby during delivery. Pregnant women with herpes or cold sores should speak with their healthcare provider about ways to reduce the risk of transmission to their baby.
Oral cancer is another condition that can occur during pregnancy. It is important to note that oral cancer is rare, but it is more likely to occur in people who smoke or use tobacco products. Pregnant women who smoke should speak with their healthcare provider about ways to quit smoking.
Other health problems and conditions, such as fever and high fever, can also occur during pregnancy. It is important for pregnant women to speak with their healthcare provider about any symptoms or concerns they may have.
In summary, pregnant women may experience a variety of oral health conditions, including canker sores, herpes, cold sores, and oral cancer. It is important for pregnant women to speak with their healthcare provider about any concerns they may have and to take steps to reduce the risk of transmission to their baby.
Canker Sores and Immune System
Canker sores are painful ulcers that develop in the mouth. While the exact cause of canker sores is unknown, research suggests that the immune system plays a role in their development. A weakened immune system can increase the risk of developing canker sores.
The immune system is responsible for protecting the body against harmful viruses and bacteria. When the immune system is weakened, it is less able to fight off infections, making it more susceptible to developing canker sores.
Some viruses, such as the herpes simplex virus, can also trigger the development of canker sores. This virus can weaken the immune system, making it easier for canker sores to develop.
It is important for pregnant women to maintain a healthy immune system to reduce the risk of developing canker sores. Eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and managing stress can all help boost the immune system. In some cases, a doctor may recommend supplements to help support the immune system during pregnancy.
In summary, a weakened immune system and certain viruses can increase the risk of developing canker sores. Maintaining a healthy immune system is important for reducing the risk of developing canker sores during pregnancy.
Research and Studies
Research on canker sores and pregnancy has been limited, but there have been some studies conducted to determine the relationship between the two. These studies have been conducted to determine the prevalence of canker sores in pregnant women, the potential causes of canker sores during pregnancy, and the impact of canker sores on pregnancy outcomes.
One study conducted in 2014 found that the prevalence of canker sores during pregnancy was 23.5%, which is higher than the prevalence of canker sores in the general population.
The study also found that the occurrence of canker sores during pregnancy was more common in the first trimester and decreased as pregnancy progressed.
Another study conducted in 2016 found that there was a significant association between canker sores and hormonal changes during pregnancy.
The study found that the increased levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy can cause changes in the immune system, which can lead to the development of canker sores.
Other studies have focused on the impact of canker sores on pregnancy outcomes. One study conducted in 2018 found that there was no significant association between canker sores and adverse pregnancy outcomes such as preterm birth, low birth weight, or fetal distress.
Overall, the research on canker sores and pregnancy is limited, but the studies conducted suggest that there is a relationship between the two.
The prevalence of canker sores during pregnancy is higher than in the general population, and hormonal changes during pregnancy can contribute to the development of canker sores. However, there is no significant association between canker sores and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Related posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can pregnancy cause mouth ulcers?
Yes, pregnancy can cause mouth ulcers. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken the immune system, making pregnant women more susceptible to canker sores.
What causes sores in the mouth during pregnancy?
The exact cause of canker sores during pregnancy is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes, stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
How do you treat mouth sores when pregnant?
Most canker sores will heal on their own within a week or two. However, there are some things pregnant women can do to relieve the pain and discomfort of mouth sores, such as using over-the-counter pain relievers, avoiding spicy or acidic foods, and rinsing with warm salt water.
Can mouth sores affect pregnancy?
Mouth sores are generally not harmful to the pregnancy, but they can be uncomfortable and make it difficult to eat and speak. If a mouth sore becomes infected, it could potentially cause more serious health problems.
Are ulcers a sign of pregnancy?
While canker sores are more common during pregnancy, they are not a sign of pregnancy. Other symptoms, such as missed periods, nausea, and fatigue, are more reliable indicators of pregnancy.
Sore tongue pregnancy third trimester
Some women may experience a sore tongue during the third trimester of pregnancy. This is often due to hormonal changes, dehydration, or a nutritional deficiency. Drinking plenty of water and eating a balanced diet can help alleviate this symptom.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.
