Pregnancy is a time of excitement and anticipation, but it also comes with its fair share of concerns and questions. One question that many pregnant women may have is whether do they drug test at every prenatal visit.
While there is no universal answer to this question, there are certain factors that can influence whether or not drug testing will be a part of your prenatal care.
Understanding Prenatal Visits is an important aspect of pregnancy, and it is essential to know what to expect during each visit. Prenatal visits are typically scheduled once a month until the 28th week of pregnancy, then every two weeks until the 36th week, and finally once a week until delivery.
During these visits, your healthcare provider will perform a variety of tests and exams to ensure that both you and your baby are healthy. Drug testing may be one of the tests that are performed, depending on your individual circumstances.

Key Takeaways
- Drug testing may or may not be a part of prenatal care, depending on individual circumstances.
- The role of drug testing in prenatal visits is to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and baby.
- Prenatal visits are an important aspect of pregnancy, and regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring the health and development of the baby.
1. Understanding Prenatal Visits
Prenatal visits are an essential part of prenatal care, and they allow healthcare providers to monitor the health of both the mother and the developing baby. These visits usually occur once a month during the first 28 weeks of pregnancy, then every two weeks until 36 weeks, and then weekly until delivery.
During each prenatal visit, the healthcare provider will check the mother’s weight, blood pressure, and urine. They will also measure the size of the uterus and listen to the baby’s heartbeat.
Some prenatal visits may include additional tests or procedures, depending on the stage of pregnancy and the health of the mother and baby.
It is important to note that drug testing is not a routine part of prenatal care or prenatal visits. However, healthcare providers may recommend drug testing if they suspect drug use or if the mother has a history of substance abuse. In such cases, drug testing may be conducted during any prenatal visit.
Overall, prenatal visits are an essential part of prenatal care and play a crucial role in ensuring the health of both the mother and the developing baby. Pregnant women should attend all scheduled prenatal appointments and communicate openly with their healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies.
2. The Role of Drug Testing in Prenatal Visits

Drug testing during prenatal visits is a common practice in many healthcare facilities. It is done to ensure the safety of both the mother and the developing fetus.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that all pregnant women be screened for illicit drug use at their first prenatal visit.
The guidelines for drug testing during prenatal visits vary depending on the healthcare facility. Some facilities may test all pregnant women at every prenatal visit, while others may only test if there is suspicion of drug use or if the mother has a history of drug use.
Consent is usually obtained before drug testing is performed. The mother must be informed of the reason for the test and the potential consequences of a positive result.
In some cases, a positive result may lead to involvement from child protective services.
Drug use during pregnancy, particularly the use of illicit drugs, can have serious consequences for both the mother and the developing fetus. Illicit drug use during pregnancy can lead to complications such as preterm labor, low birth weight, and developmental delays in the child.
Addiction and substance use disorders are also common among pregnant women. Drug testing during prenatal visits can help identify these issues early on and allow for appropriate interventions.
Urine drug screens are the most commonly used method for drug testing during prenatal visits. These tests can detect a wide range of illicit drugs and prescription medications.
In conclusion, drug testing during prenatal visits plays an important role in ensuring the safety of both the mother and the developing fetus. It can help identify drug use and addiction early on, allowing for appropriate interventions to be made.
However, it is important to obtain consent and follow appropriate guidelines for drug testing to ensure ethical and legal practices.
3. Health Checks During Prenatal Visits
During prenatal visits, healthcare providers perform a variety of health checks to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. These checks include regular monitoring of weight, blood pressure, and urine samples.
Urine samples are typically collected at every prenatal visit to check for signs of infection, dehydration, and proteinuria. Proteinuria is a condition in which protein is present in the urine, which can be a sign of preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication.
Blood tests may also be performed to check for anemia, gestational diabetes, and other conditions. These tests can help identify any potential risks to the mother and baby and allow for early intervention and treatment.
In addition to these routine checks, healthcare providers may also perform additional tests or screenings based on the mother’s medical history, risk factors, or symptoms. For example, women with a history of high blood pressure may be monitored more closely for signs of preeclampsia.
Overall, regular prenatal visits and health checks are essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a safe delivery. By monitoring the mother’s health and the development of the fetus, healthcare providers can identify and address any potential issues early on, leading to the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
4. Important Examinations During Prenatal Visits
Prenatal visits are crucial for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. During these visits, healthcare providers will perform a variety of examinations to monitor the progress of the pregnancy and ensure that both mother and baby are healthy.
Some of the important examinations that are typically performed during prenatal visits include:
Physical Exam
At each prenatal visit, the healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to check the mother’s overall health. This may include taking the mother’s blood pressure, measuring her weight and height, and checking her heart and lungs.
The healthcare provider will also examine the mother’s abdomen to check the size and position of the uterus and the growth of the fetus.
Pelvic Exam
During the first prenatal visit, the healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to check the size and shape of the mother’s pelvis. This can help determine if there are any potential problems with delivery.
However, pelvic exams are typically not performed at every prenatal visit unless there is a specific concern.
Blood Tests

Blood tests are an important part of prenatal care and are typically performed at the first prenatal visit. These tests can help determine the mother’s blood type and Rh factor, as well as check for any infections or diseases that could affect the pregnancy, such as HIV or syphilis.
Pap Smear
A pap smear is a test that checks for abnormal cells in the cervix. This test is typically performed at the first prenatal visit and may be repeated later in the pregnancy if necessary.
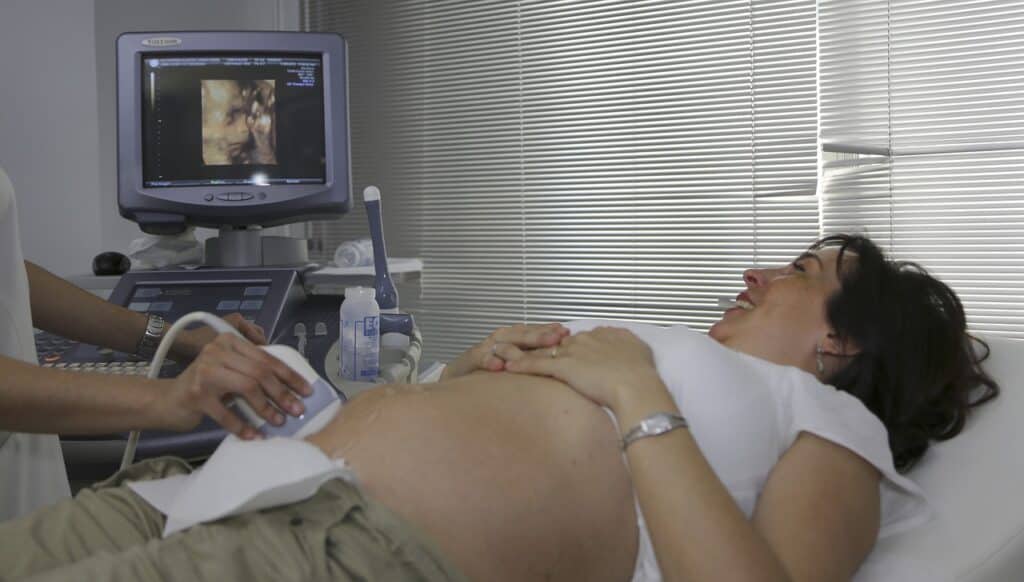
Ultrasound

Ultrasound is a diagnostic test that uses sound waves to create images of the developing fetus. This test is typically performed at least once during the pregnancy to check the growth and development of the fetus and to screen for any potential problems.
Overall, prenatal visits are an important part of ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. By monitoring the progress of the pregnancy and performing necessary examinations, healthcare providers can catch any potential problems early and take steps to ensure the best possible outcome for both mother and baby.
5. Concerns Regarding Drug Use During Pregnancy
Drug use during pregnancy can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby. It is important for pregnant women to avoid using drugs, including alcohol and tobacco, to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Drug use during pregnancy can lead to various complications, including premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental delays. Women who use drugs during pregnancy are also at a higher risk of developing health issues such as diabetes and infections caused by bacteria.
In addition to the health risks, drug use during pregnancy can also result in legal consequences. Women who use drugs during pregnancy may be arrested and face custody battles for their children.
Child Protective Services may also become involved, which can lead to the removal of the child from the mother’s care.
It is important for healthcare providers to address drug use during prenatal visits and offer treatment options for women who struggle with addiction. However, ethical concerns may arise when healthcare providers involve law enforcement or child protective services in cases of drug use during pregnancy.
Overall, it is crucial for pregnant women to avoid drug use and seek help if they struggle with addiction. Healthcare providers can play a vital role in addressing drug use during pregnancy and offering support and resources for women in need.
6. Monitoring Baby’s Growth and Development

During prenatal visits, healthcare providers monitor the growth and development of the baby. This is done by measuring the size of the uterus, checking the baby’s heartbeat, and performing ultrasounds.
These tests can help identify any potential issues with the baby’s growth or development.
If a woman is carrying twins or multiples, more frequent ultrasounds may be performed to monitor the growth and development of each baby. This is because twins and multiples are at a higher risk of certain complications, such as premature birth and low birth weight.
In addition to monitoring the baby’s growth, prenatal visits also provide an opportunity to screen for birth defects. This can be done through a combination of ultrasounds and blood tests, which can detect certain genetic disorders and other abnormalities.
Overall, regular prenatal visits are important for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. By monitoring the baby’s growth and development, healthcare providers can identify any potential issues and take steps to address them before they become more serious.
7. Additional Aspects of Prenatal Care

Apart from drug testing, prenatal care involves several other aspects that are crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a safe delivery. The following are some additional aspects of prenatal care that pregnant women should be aware of:
First Trimester
During the first trimester, healthcare providers usually perform a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. This includes assessing the woman’s overall health, identifying any pre-existing medical conditions, and determining the due date.
The provider may also order blood tests to check for pregnancy hormone levels, Rh status, and other conditions that may affect the pregnancy.
Third Trimester
In the third trimester, healthcare providers may perform additional tests to monitor the baby’s growth and development. This may include measuring the size of the uterus, checking the baby’s heart rate with a Doppler, and performing ultrasounds to visualize the baby’s position and estimate its weight.
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) recommends that pregnant women receive regular prenatal care throughout their pregnancy. This includes regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, as well as appropriate screening tests and vaccinations.
Exercise
Exercise is an important aspect of prenatal care and can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. However, pregnant women should consult with their healthcare provider before starting or continuing any exercise program.
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are an important aspect of prenatal care and can help protect both the mother and the baby from certain infections. Pregnant women should receive the flu vaccine and the Tdap vaccine during pregnancy, as recommended by ACOG.
Medications
Some medications may be harmful to the developing fetus and should be avoided during pregnancy. Pregnant women should always consult with their healthcare provider before taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Morning Sickness
Morning sickness is a common symptom of early pregnancy and can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications in some cases. Pregnant women should discuss any concerns about morning sickness with their healthcare provider.
Tuberculosis and Hepatitis
Pregnant women should be screened for tuberculosis and hepatitis during prenatal care, as these infections can be harmful to both the mother and the baby.
Rh Status
Rh status is an important aspect of prenatal care and can affect the baby’s health. Women who are Rh-negative may require additional monitoring and treatment during pregnancy to prevent complications.
Pregnancy Hormone
Pregnancy hormone levels are routinely checked during prenatal care to ensure a healthy pregnancy and identify any potential complications.
Dehydrated
Dehydration can be harmful during pregnancy and can lead to complications such as preterm labor. Pregnant women should drink plenty of fluids and discuss any concerns about dehydration with their healthcare provider.
Preterm Labor
Preterm labor is a serious complication of pregnancy and can lead to premature birth and other complications. Pregnant women should be aware of the signs and symptoms of preterm labor and seek medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms.
Related Posts:
- Does OBGYN Drug Test Urine? A Clear Answer for Expecting Mothers
- Do OB/GYNs Drug Test During Pregnancy? Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Medicaid drug test pregnant women?
Medicaid does not routinely drug test pregnant women. However, individual states may have their own policies regarding drug testing during pregnancy. It is important to check with your state’s Medicaid program to understand their policies.
Why do doctors take urine samples during prenatal visits?
Doctors take urine samples during prenatal visits to check for various health conditions that could affect the pregnancy. These include infections, protein levels, and glucose levels. Additionally, doctors may test for drugs to ensure the safety of the mother and the baby.
What happens if you test positive for drugs while pregnant?
If a pregnant woman tests positive for drugs, the doctor will likely discuss the results with her and offer resources for treatment and support. In some cases, Child Protective Services may become involved if there is concern for the safety and well-being of the baby.
What substances do doctors test for during prenatal visits?
Doctors typically test for a variety of substances during prenatal visits, including drugs such as marijuana, cocaine, and opioids. They may also test for tobacco and alcohol use.
Can you refuse a drug test from your doctor while pregnant?
While it is ultimately up to the individual, it is important to understand that refusing a drug test during pregnancy may raise concerns about the safety of the baby. It is recommended to discuss any concerns or questions with your doctor.
How often are drug tests performed during prenatal visits?
The frequency of drug tests during prenatal visits may vary depending on individual circumstances and medical history. However, it is common for doctors to test for drugs at the first prenatal visit and then periodically throughout the pregnancy.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.
