Urine drug testing is a common practice in medical settings to detect drug use among patients. OBGYNs, or obstetrician-gynecologists, are medical professionals who specialize in women’s reproductive health.
OBGYNs conduct various tests during pregnancy to ensure the health of the mother and the baby. One question that may arise is whether OBGYNs drug test urine during pregnancy.
Urine drug testing is a laboratory test that detects the presence of drugs or their metabolites in a person’s urine sample. The test is commonly used in medical settings, workplace drug testing, and drug rehabilitation programs.
Urine drug testing is a non-invasive and relatively simple procedure that can detect drug use within a certain period, depending on the drug and the frequency of use.
Key Takeaways
- OBGYNs may conduct urine drug tests during pregnancy to ensure the health of the mother and the baby.
- Urine drug testing can detect a wide range of drugs, including prescription drugs, illegal drugs, and alcohol.
- Drug use during pregnancy can have serious consequences for the health of both the mother and the baby.
Understanding Urine Drug Testing
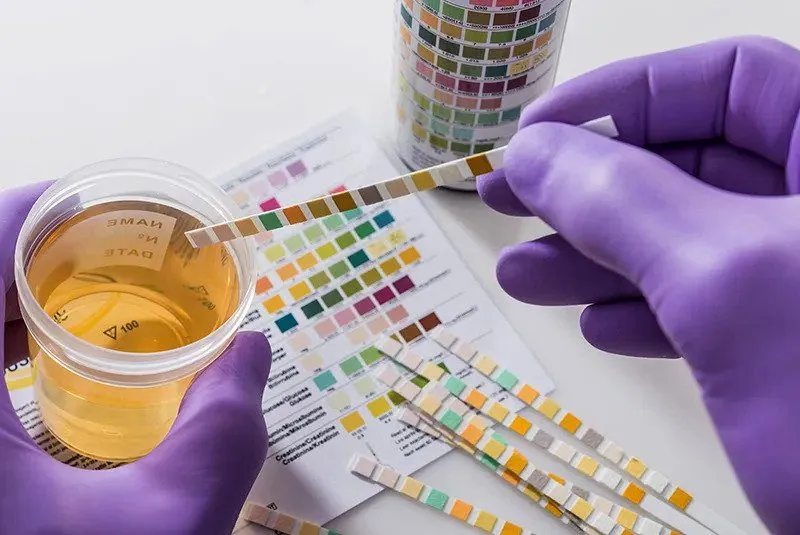

Urine drug testing is a common method used to detect the presence of drugs in a person’s system. It involves the collection of a urine sample, which is then analyzed for the presence of drugs or their metabolites.
The urine sample is collected in a sterile cup and is typically tested in a laboratory. The analysis is performed using immunoassays, which are tests that use antibodies to detect the presence of drugs in the urine.
It is important to note that urine drug testing is not always accurate and can produce false-positive or false-negative results. A false-positive result is when the test indicates the presence of drugs when there are none, while a false-negative result is when the test fails to detect the presence of drugs when they are present in the urine sample.
Technicians are responsible for collecting and handling the urine sample, while medical review officers are responsible for interpreting the results of the drug test.
Overall, urine drug testing is a useful tool in detecting drug use, but it is important to understand its limitations and potential for false results.
Why OBGYNs Conduct Drug Tests
Drug testing is a common practice in the healthcare industry, and OBGYNs are no exception. OBGYNs conduct drug tests for several reasons, including ensuring the health and safety of both the mother and the unborn child.
Pregnancy is a critical time for women, and drug use can pose significant risks to both the mother and the fetus. OBGYNs may conduct drug tests to identify any substance use that may harm the mother or the baby during pregnancy.
Additionally, drug use during pregnancy can lead to addiction, which can have long-term consequences for both the mother and the child.
Drug testing can also help identify pregnant women who are at risk of substance use. Risk factors for drug use during pregnancy include a history of substance use, mental health issues, and social and economic factors.
OBGYNs may use drug testing to identify these risk factors and provide appropriate care and support to pregnant women who need it.
Finally, OBGYNs may conduct drug tests when there is suspicion of drug use. Suspicion can arise from several factors, including a patient’s behavior, medical history, or physical symptoms.
Drug testing can help OBGYNs confirm or rule out drug use and provide appropriate care and support to their patients.
Overall, drug testing is an essential tool for OBGYNs to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the unborn child.
By identifying substance use and risk factors, OBGYNs can provide appropriate care and support to pregnant women who need it and help prevent long-term consequences of drug use.
Drugs Tested in Urine Samples
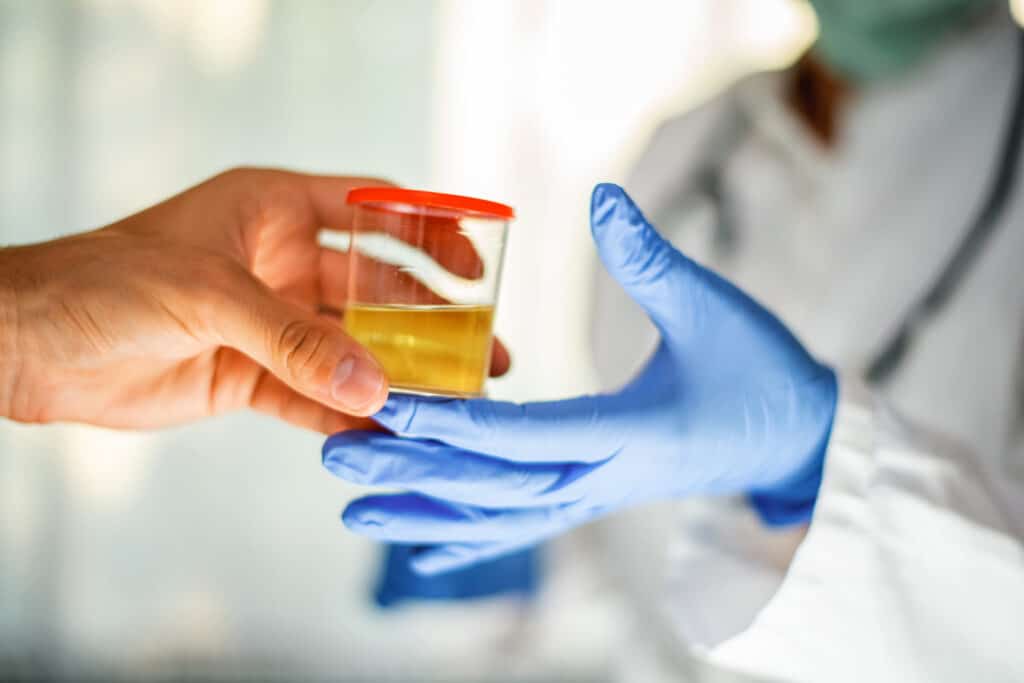

When visiting an OBGYN, patients may wonder if their urine will be tested for drugs. In most cases, a urine drug test is not a routine part of prenatal care.
However, there are certain situations where a drug test may be required.
The following drugs are commonly tested for in urine samples:
- Cocaine: Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant drug that can cause serious health problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Alcohol: Alcohol is a legal drug that can be harmful to a developing fetus. Pregnant women are advised to abstain from alcohol.
- Methadone: Methadone is a synthetic opioid used to treat addiction to heroin and other opioids.
- Illegal drugs: Illegal drugs such as heroin, methamphetamine, and PCP can cause serious harm to a developing fetus.
- Amphetamines: Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that can cause serious health problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Opioids: Opioids are a class of drugs that include prescription painkillers and heroin. These drugs can cause serious harm to a developing fetus.
- Barbiturates: Barbiturates are a class of drugs that are used to treat anxiety and insomnia. These drugs can cause serious health problems, including addiction and overdose.
- Marijuana/Cannabinoids: Marijuana is a drug that is legal in some states for medical and recreational use. However, it can cause serious harm to a developing fetus.
- PCP: PCP is a hallucinogenic drug that can cause serious health problems, including seizures and coma.
- Nicotine: Nicotine is a legal drug found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. Smoking during pregnancy can cause serious harm to a developing fetus.
- Heroin: Heroin is a highly addictive opioid drug that can cause serious health problems, including overdose and death.
- Prescription medications: Prescription medications such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants can cause serious harm to a developing fetus if not taken as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that are used to treat anxiety and insomnia. These drugs can cause serious health problems, including addiction and overdose.
It is important to note that drug testing policies and procedures may vary depending on the healthcare provider and the state in which they practice. Patients should always discuss any concerns or questions about drug testing with their healthcare provider.
Impact of Drug Use on Pregnancy
Drug use during pregnancy can have serious consequences for both the mother and the developing fetus. The use of illicit drugs, prescription medications, and even some over-the-counter drugs can all pose risks to the health of the mother and the baby.
Pregnant women who use drugs are at increased risk of experiencing complications during pregnancy and childbirth. These complications can include preterm labor, low birth weight, placental abruption, and stillbirth.
Additionally, drug use during pregnancy can increase the risk of birth defects and developmental delays in the baby.
Illicit drugs such as cocaine, heroin, and methamphetamine can have particularly harmful effects on the developing fetus. These drugs can cross the placenta and directly affect the baby’s growth and development.
They can also cause problems with the baby’s brain development and increase the risk of behavioral and cognitive problems later in life.
Prescription medications can also be harmful if used improperly during pregnancy. Some medications, such as opioids and benzodiazepines, can cause withdrawal symptoms in the baby after birth. Other medications, such as certain antidepressants, can increase the risk of birth defects.
It is important for pregnant women to discuss any drug use, including prescription medications, with their healthcare provider.
Healthcare providers can help women make informed decisions about the risks and benefits of using medications during pregnancy and can provide support for women who are struggling with drug addiction.
Overall, drug use during pregnancy can have serious and long-lasting effects on both the mother and the baby. Pregnant women should take steps to protect their health and the health of their baby by avoiding drug use and seeking help if they are struggling with addiction.
Procedure and Accuracy of Urine Drug Test
When conducting a urine drug test, the first step is to collect a urine sample from the patient. The urine sample is then analyzed to detect the presence of drugs or drug metabolites in the patient’s system.
Urine drug tests are commonly used by OBGYNs to monitor patients who are taking prescription medications or who have a history of substance abuse.
The accuracy of urine drug tests can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of drug being tested for, the timing of the test, and the quality of the urine sample.
One potential issue with urine drug tests is the possibility of false-positive or false-negative results. False-positive results occur when the test indicates the presence of a drug in the patient’s system, even though the patient has not actually used the drug.
False-negative results occur when the test fails to detect the presence of a drug in the patient’s system, even though the patient has used the drug.
To minimize the risk of false-positive or false-negative results, it is important to follow proper procedures when collecting and analyzing urine samples.
This includes ensuring that the urine sample is collected at the appropriate time, that the sample is not contaminated, and that the sample is analyzed using reliable testing methods.
It is also important to note that certain factors can affect the accuracy of urine drug tests. For example, taking certain supplements or medications can cause false-positive results, while tampering with the urine sample or altering its temperature can cause false-negative results.
Overall, while urine drug tests can be an effective tool for monitoring patients’ drug use, it is important to understand the limitations of these tests and to use them in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and clinical assessments.
Legal Aspects of Drug Testing in OBGYN Practice
Drug testing is a common practice in many healthcare settings, including OBGYN offices. However, there are legal considerations that must be taken into account when implementing drug testing policies.
Under federal law, drug testing is permitted if it is conducted in accordance with established guidelines and policies. These guidelines should be based on sound medical principles and should be applied equally to all patients.
In addition, healthcare providers must obtain informed consent from patients before conducting drug testing. This means that patients must be informed of the purpose and nature of the drug testing, the potential risks and benefits, and their right to refuse testing.
Doctors and other healthcare providers who conduct drug testing must also comply with state and local laws governing drug testing in the workplace. For example, some states require that employers provide employees with written notice of drug testing policies and procedures.
Employers and healthcare providers must also ensure that drug testing is conducted in a manner that protects patient privacy and confidentiality. This includes ensuring that drug test results are kept confidential and are only shared with authorized individuals.
In summary, drug testing in OBGYN practice is legal if conducted in accordance with established guidelines and policies, with informed consent from patients, and in compliance with state and local laws.
Healthcare providers must also ensure that drug testing is conducted in a manner that protects patient privacy and confidentiality.
Alternatives to Urine Drug Testing
While urine drug testing is a common method used by OBGYNs to screen for substance abuse during pregnancy, there are alternative methods available. These methods can be useful for patients who are uncomfortable with urine testing or have difficulty providing a urine sample.
1. Blood Sample
One alternative to urine drug testing is a blood sample. Blood tests can detect a wider range of substances and can provide more accurate results. However, blood tests are more invasive than urine tests and can be more expensive.
2. At-Home Test
Another option is an at-home drug test. These tests are available over-the-counter and can be performed in the privacy of the patient’s own home. At-home tests are less invasive than urine or blood tests and can provide results within minutes.
However, they may not be as accurate as laboratory testing and may not detect all substances.
3. Pregnancy Tests
Pregnancy tests can also be used as an alternative to urine drug testing. While pregnancy tests are not designed to detect drugs, they can detect hCG, a hormone produced during pregnancy. If a patient tests positive for hCG but is not pregnant, it could be an indication of drug use.
Overall, while urine drug testing is a common method used by OBGYNs, there are alternative methods available. Patients should discuss their options with their healthcare provider to determine which method is best for them.
Cost and Efficiency of Urine Drug Testing
Urine drug testing is a common practice in obstetrics and gynecology clinics. It is a quick, easy, and painless way to screen for drug use during pregnancy. However, cost and efficiency are important factors to consider when implementing this type of testing.
Urine drug testing can be expensive, especially if it is done frequently. The cost of the test can vary depending on the type of drug being tested for and the laboratory performing the test. Some insurance plans may cover the cost of the test, but not all plans do.
Patients should check with their insurance provider to determine if the test is covered.
Despite the potential cost, urine drug testing is a cost-effective way to screen for drug use during pregnancy. It can identify drug use early on, allowing for intervention and treatment if necessary. This can lead to better outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Efficiency is another important factor to consider. Urine drug testing is a quick and easy process. The patient provides a urine sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are typically available within a few days.
Overall, urine drug testing is a valuable tool for obstetrics and gynecology clinics. While it can be expensive, it is a cost-effective way to screen for drug use during pregnancy. It is also quick and easy, making it an efficient screening method.
Treatment and Support for Drug Use During Pregnancy
If a pregnant woman tests positive for drug use, it is important for her to receive proper treatment and support to ensure the health of both herself and her unborn child. The treatment plan will depend on the severity of the addiction and the type of substance abuse involved.
A physician or health care provider may recommend a variety of treatment options, including medication-assisted treatment, counseling, and support groups. Medication-assisted treatment involves the use of medications to help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings.
Counseling and support groups can help the woman address the underlying issues that led to drug use and provide emotional support during the recovery process.
It is important for the woman to receive ongoing monitoring and support throughout her pregnancy and beyond. This can include regular check-ups with a health care provider, drug testing, and referrals to additional resources as needed.
Overall, the goal of treatment and support for drug use during pregnancy is to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. With proper care and support, women can successfully overcome addiction and give birth to healthy babies.
Related Posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
What drugs do OBGYNs test for during prenatal visits?
OBGYNs typically test for a variety of drugs during prenatal visits, including but not limited to marijuana, cocaine, opioids, and amphetamines. The specific drugs tested for may vary depending on the healthcare provider’s policies and the patient’s medical history.
Can hospitals drug test newborns without parental consent?
In some cases, hospitals may drug test newborns without parental consent if there is a suspicion of drug use during pregnancy or if the mother’s drug test during prenatal care was positive. However, laws regarding newborn drug testing without consent vary by state and hospital policy.
How long do drugs stay in a newborn’s urine?
The length of time drugs stay in a newborn’s urine can vary depending on the type of drug, the mother’s usage patterns, and the baby’s metabolism. Generally, drugs can be detected in a newborn’s urine for up to a few days to a few weeks after birth.
Do doctors test for drugs during urinalysis?
Doctors may test for drugs during urinalysis if there is a suspicion of drug use or if it is part of routine prenatal care. However, it is important to note that not all urinalysis tests include drug testing.
What is the purpose of OBGYNs testing urine during prenatal visits?
The purpose of OBGYNs testing urine during prenatal visits is to monitor the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Urine tests can detect a variety of health issues, including infections, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia. Additionally, urine tests can be used to screen for drug use during pregnancy.
Is drug testing part of routine care during labor and delivery?
Drug testing is not typically part of routine care during labor and delivery, but it may be performed if there is a suspicion of drug use or if the mother’s drug test during prenatal care was positive.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.
