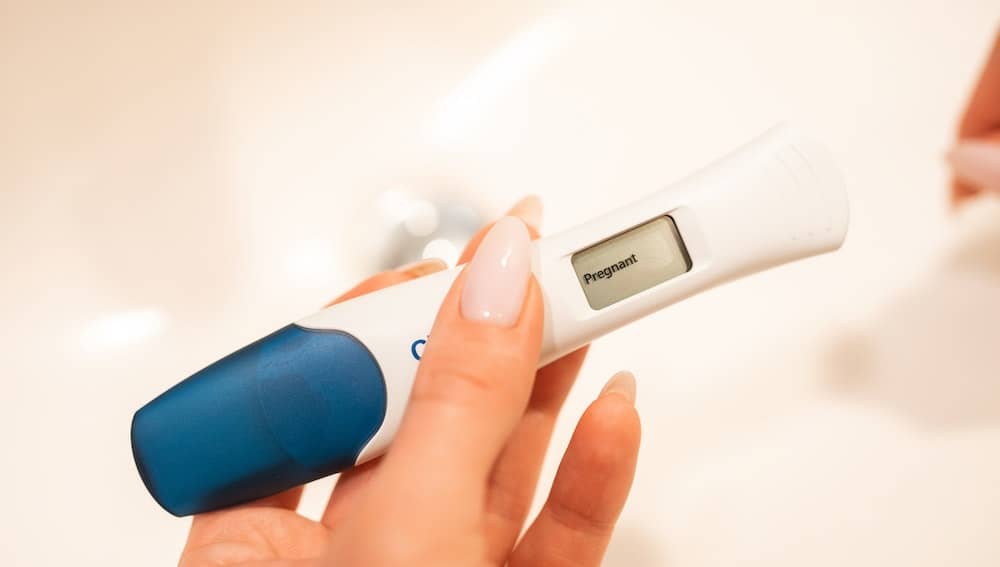
Yeast infections are a common condition that can affect women at any age. They are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which can lead to symptoms such as itching, burning, and discharge.
While yeast infections are generally harmless, they can be uncomfortable and even painful. Additionally, some women may wonder if having a yeast infection can affect the results of a pregnancy test.
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which is naturally present in the body. Certain factors, such as taking antibiotics or having a weakened immune system, can cause the fungus to grow out of control, leading to a yeast infection.
Symptoms of a yeast infection can include itching, burning, and discharge. While yeast infections are generally harmless, they can be uncomfortable and even painful.
Some women may wonder if having a yeast infection can affect the results of a pregnancy test. The short answer is no. Yeast infections do not contain the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is the hormone that pregnancy tests detect.
However, if a woman is experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection, such as itching or burning, she may want to wait until her symptoms have resolved before taking a pregnancy test to avoid any confusion or misinterpretation of the results.
Key Takeaways
- Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which can lead to symptoms such as itching, burning, and discharge.
- Yeast infections do not contain the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is the hormone that pregnancy tests detect.
- Women who are experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection may want to wait until their symptoms have resolved before taking a pregnancy test to avoid any confusion or misinterpretation of the results.
Understanding Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are a common condition that affects many women at some point in their lives. Yeast is a type of fungus that is normally present in the vagina in small amounts.
However, when the balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina is disrupted, yeast can overgrow and cause an infection. The most common type of yeast that causes vaginal infections is Candida albicans.
The symptoms of a yeast infection can vary from person to person, but some common signs include itching, burning, and soreness in the vulva and vagina.
Other symptoms may include redness, swelling, and a rash. Women with yeast infections may also experience a thick, white, odorless discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
Yeast infections can be uncomfortable and frustrating, but they are generally not serious. However, in some cases, they can lead to complications.
For example, if a pregnant woman has a yeast infection, it can increase the risk of premature delivery or a low birth weight baby.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing a yeast infection, including taking antibiotics, having a weakened immune system, and using certain types of birth control.
Women who are pregnant may also be more susceptible to yeast infections due to hormonal changes in the body.
If you suspect that you have a yeast infection, it is important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment typically involves antifungal medication, which can be taken orally or applied topically.
In some cases, lifestyle changes such as wearing loose-fitting clothing and avoiding scented products may also be recommended to help prevent future infections.
In conclusion, yeast infections are a common condition that can cause discomfort and irritation. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, they can be effectively managed.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have a yeast infection, particularly if you are pregnant or have other underlying health conditions.
Yeast Infections and Pregnancy
Yeast infections are common among women, and pregnancy can increase the likelihood of developing one. Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans, which is naturally present in the vagina.
When the balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina is disrupted, it can lead to an overgrowth of yeast and the development of an infection.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can affect the pH balance of the vagina, making it more susceptible to yeast infections.
Additionally, high estrogen levels can promote the growth of yeast. Yeast infections during pregnancy are more common in the second trimester and third trimester, but can occur at any time.
While yeast infections do not typically affect pregnancy tests, it is important to note that other infections during pregnancy can have an impact. Infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis can cause false negative results on pregnancy tests.
It is important for pregnant women to receive regular prenatal care and testing to ensure the health of both the mother and developing baby.
Untreated yeast infections during pregnancy can also lead to complications. In severe cases, yeast infections can lead to preterm labor and low birth weight.
It is important for pregnant women to seek medical treatment if they suspect they have a yeast infection.
In summary, yeast infections are common during pregnancy and can be caused by hormonal changes and high estrogen levels.
While yeast infections do not typically affect pregnancy tests, other infections during pregnancy can cause false negative results. It is important for pregnant women to receive regular prenatal care and testing to ensure the health of both the mother and developing baby.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If a pregnant woman suspects that she has a yeast infection, it is important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
A doctor can confirm whether the symptoms are due to a yeast infection or another condition, such as bacterial vaginosis.
During the diagnosis, the doctor may perform a pelvic exam and take a sample of vaginal discharge to be examined under a microscope. In some cases, the doctor may also order a blood test to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for yeast infections during pregnancy typically involves the use of antifungal medication. Over-the-counter medications, such as antifungal creams and suppositories, may be used in mild cases.
However, oral medication, such as fluconazole, is generally not recommended during pregnancy.
Instead, doctors may prescribe topical antifungal creams or suppositories, such as clotrimazole or miconazole. These medications are inserted into the vagina and are usually used for 7 to 14 days. Some women may experience mild irritation or discomfort when using these medications.
In severe cases, doctors may prescribe a medication called Diflucan. This is an oral medication that is taken once or twice during pregnancy. However, it should only be used under close medical supervision.
Overall, the treatment of yeast infections during pregnancy is safe and effective. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most women can expect to recover from a yeast infection without any complications.
Yeast Infections and Pregnancy Tests
Yeast infections are a common occurrence in women, especially during pregnancy. It is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the vaginal area, leading to itching, burning, and discharge.
While yeast infections do not directly affect the accuracy of a pregnancy test, there are several factors to consider.
Firstly, if a woman is experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection, it is important to address it before taking a pregnancy test.
The presence of discharge or blood from the infection can interfere with the results of the test, leading to false negatives or false positives.
Secondly, certain medications used to treat yeast infections can also affect the accuracy of a pregnancy test. For example, antifungal creams containing miconazole or clotrimazole can cause a false positive result.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication while trying to conceive or during pregnancy.
Thirdly, if a woman is pregnant and experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection, it is important to seek medical attention. Untreated yeast infections can lead to complications during pregnancy, such as preterm labor or low birth weight.
In summary, while yeast infections do not directly affect the accuracy of a pregnancy test, it is important to address any symptoms before taking the test and to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication.
If a woman is pregnant and experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection, prompt medical attention is necessary to prevent complications.
Risk Factors and Prevention
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a yeast infection during pregnancy.
These include:
- High levels of estrogen: This hormone can promote the growth of yeast, which can lead to an overgrowth of the fungus in the vaginal area.
- Antibiotic use: Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body, which can lead to an overgrowth of yeast.
- Weakened immune system: Pregnant women with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or diabetes, may be more susceptible to yeast infections.
- Tight clothing: Wearing tight-fitting clothing, especially synthetic fabrics, can create a warm and moist environment that is conducive to the growth of yeast.
- Poor hygiene: Failing to keep the genital area clean and dry can increase the risk of developing a yeast infection.
- Sexual activity: Intercourse can introduce bacteria and other organisms into the vaginal area, which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and increase the risk of developing a yeast infection.
- Use of certain medications: Steroids and birth control pills can alter the body’s natural balance of hormones, which can lead to an overgrowth of yeast.
To prevent yeast infections during pregnancy, it is important to practice good hygiene and avoid the risk factors mentioned above. Some tips for preventing yeast infections include:
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics, such as cotton.
- Avoiding the use of vaginal sprays, douches, and bubble baths.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and blood sugar level.
- Practicing safe sex by using condoms and avoiding sexual activity with partners who have STDs.
- Resting and reducing stress as much as possible.
- Regularly visiting a healthcare provider for checkups and pelvic exams.
It is important to note that yeast infections during pregnancy can lead to complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease and painful urination. Therefore, pregnant women should take steps to prevent and treat yeast infections as soon as possible.
Related Posts:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a yeast infection affect pregnancy test results?
No, a yeast infection does not affect the accuracy of a pregnancy test. Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which does not produce the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) that is detected by pregnancy tests.
Can monistat affect pregnancy test accuracy?
No, using Monistat, an over-the-counter medication for yeast infections, does not affect the accuracy of a pregnancy test. Monistat works locally in the vagina and does not interfere with the production of hCG in the body.
Can pregnancy cause yeast infections?
Yes, pregnancy can increase the risk of developing a yeast infection. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can alter the pH balance of the vagina, making it more susceptible to overgrowth of yeast.
Pregnant women should speak with their healthcare provider if they suspect they have a yeast infection.
Can a yeast infection cause a miscarriage?
No, a yeast infection does not directly cause a miscarriage. However, if left untreated, a yeast infection can lead to complications that may increase the risk of miscarriage. Pregnant women with symptoms of a yeast infection should seek medical attention.
Can a yeast infection cause a false negative pregnancy test?
No, a yeast infection does not cause a false negative pregnancy test. Pregnancy tests detect the presence of hCG in urine or blood, which is not affected by a yeast infection.
Can an infection cause a negative pregnancy test?
It depends on the type of infection. Some infections, such as urinary tract infections or kidney infections, may cause a negative pregnancy test if they interfere with the production of hCG in the body. However, most infections do not affect pregnancy test results.
If a person suspects they have an infection and are pregnant, they should speak with their healthcare provider.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.