Ultrasound is a common medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures. It is most commonly associated with pregnancy, where it is used to monitor the development of the fetus. However, ultrasound can also be used to examine other parts of the body, including the hair. So, Lets discuss what does hair look like on an ultrasound.
Hair detection in ultrasounds is possible due to the fact that hair has a different density than other tissues in the body. This density difference causes the hair to appear as a bright white line on the ultrasound image. While hair detection is not a routine part of most ultrasounds, it can be useful in certain situations, such as when monitoring premature babies or when looking for signs of fetal abnormalities.
Key Takeaways
- Hair can be detected on ultrasound images due to its different density compared to other tissues in the body.
- Ultrasound is commonly used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy, but can also be used to examine other parts of the body.
- Hair detection is not a routine part of most ultrasounds, but can be useful in certain situations.
Understanding Ultrasound
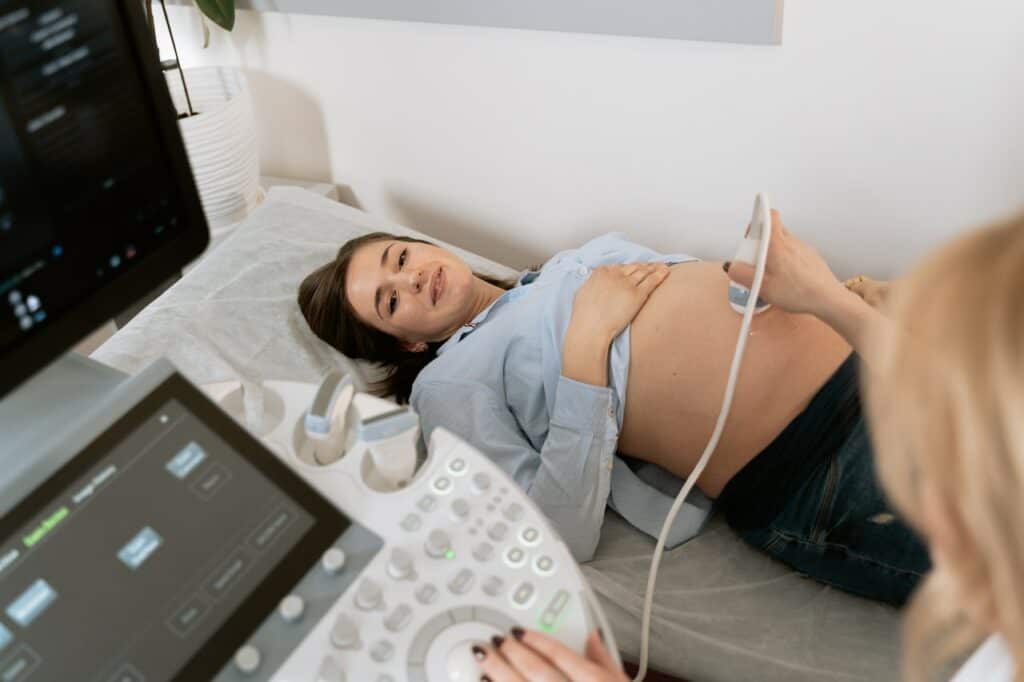

Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures of the body. These sound waves are emitted by a transducer, which is a handheld device that is placed on the skin. The sound waves then bounce off the internal structures and are picked up by the transducer, which sends the information to a computer to create an image.
There are different types of ultrasound imaging techniques, including 2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound. 2D ultrasound is the most commonly used technique and produces a flat, two-dimensional image. 3D ultrasound produces a three-dimensional image, while 4D ultrasound produces a real-time 3D image that shows movement.
Sonography is the practice of performing ultrasound imaging, and ultrasound technicians are trained to use the equipment and interpret the images produced. They play an important role in diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions.
Ultrasound imaging is safe and non-invasive, making it a preferred imaging technique for many medical conditions. It is commonly used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy, diagnose conditions such as gallstones and kidney stones, and guide procedures such as biopsies.
The images produced by ultrasound can vary in quality depending on the type of ultrasound used, the skill of the technician, and the condition being imaged. However, ultrasound is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions and is an important part of modern medical practice.
Hair Detection in Ultrasounds
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal organs and structures of the body. It is commonly used during pregnancy to monitor the growth and development of the fetus. While ultrasounds are primarily used to visualize the bones, organs, and tissues of the body, they can also detect hair on the fetus.
Hair on ultrasound appears as a fine, wispy texture that can be seen in black and white images. Hair growth can be detected as early as 14 weeks gestation, although it is more commonly seen after 20 weeks. Hair follicles appear as small, round structures that are densely packed together.
The density of hair on ultrasound can vary depending on the position of the fetus and the angle of the ultrasound probe. White strands may be seen in areas where the hair is less dense, while areas with more hair may appear as solid black regions.
It is important to note that hair detection on ultrasound is not a reliable indicator of fetal health or development. While it can provide valuable information about the fetus, it should be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical observations.
In summary, hair detection on ultrasound is possible and can provide valuable information about fetal development. However, it should be interpreted cautiously and in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical observations.
Role of Ultrasound in Pregnancy

Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. In pregnancy, ultrasound is used to monitor the growth and development of the baby, as well as to check for any abnormalities or complications.
During an ultrasound scan, the technician will apply a gel to the mother’s abdomen and use a handheld device called a transducer to send sound waves through the uterus. The sound waves bounce off the baby and other structures in the uterus, creating an image that can be seen on a monitor.
Ultrasound scans are typically performed at different stages of pregnancy to monitor the baby’s growth and development. In the first trimester, ultrasound can be used to confirm the pregnancy and determine the gestational age of the baby. In the second trimester, ultrasound can be used to check for any abnormalities in the baby’s organs, as well as to determine the baby’s sex. In the third trimester, ultrasound can be used to monitor the baby’s growth and position, as well as to check the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
One of the most important measurements taken during a baby ultrasound is the size of the baby’s head. This measurement can help determine the baby’s gestational age and ensure that the baby is growing at a normal rate. In addition to measuring the baby’s head, ultrasound can also be used to check the baby’s position in the uterus, as well as to measure the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the baby.
Overall, ultrasound plays a critical role in monitoring the health and development of the baby during pregnancy. By providing detailed images of the baby and other structures in the uterus, ultrasound can help detect any potential problems early on, allowing for prompt treatment and better outcomes for both mother and baby.
Understanding Fetal Hair Development
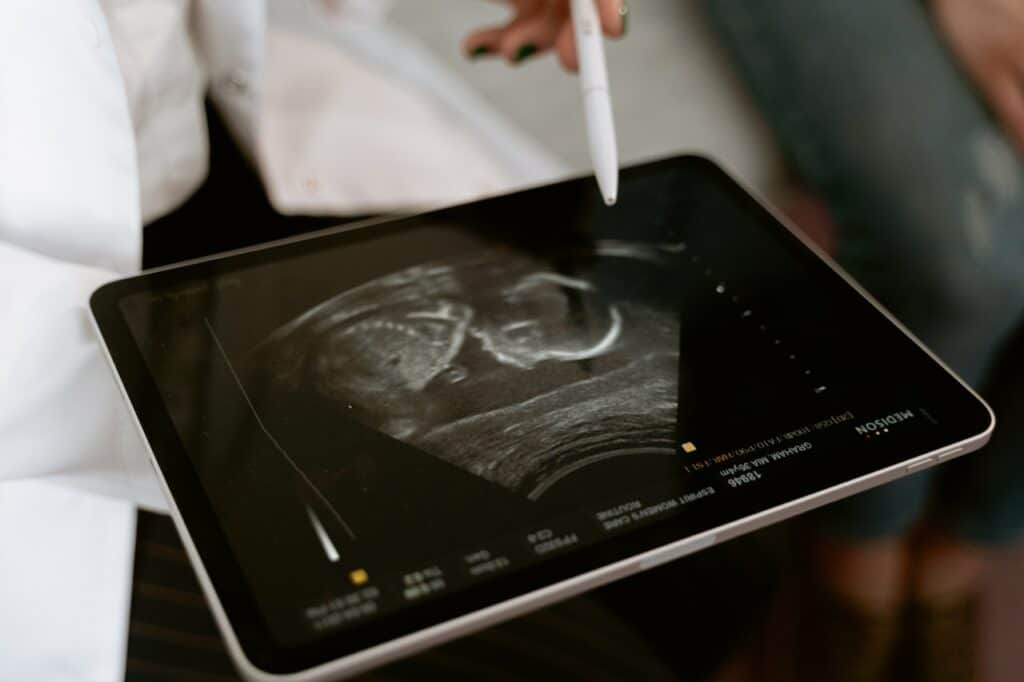
Fetal hair development is a fascinating process that occurs during pregnancy. It is important to understand the different types of hair that can develop in a fetus, as well as the factors that can influence hair growth and appearance.
Types of Fetal Hair
There are two types of hair that can develop in a fetus: lanugo and terminal hair. Lanugo is the soft, downy hair that covers a fetus’s body from around the 12th week of gestation until the 20th week. Terminal hair, on the other hand, is the thicker, coarser hair that grows on the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
Factors That Influence Hair Growth and Appearance
Genetics play a significant role in determining a fetus’s hair growth and appearance. Hair color, texture, and thickness are all determined by an individual’s genetic makeup. Additionally, the amount of hair a fetus has can be influenced by gender, with male fetuses generally having more hair than female fetuses.
Baby Hair Growth
After birth, a baby’s hair growth can vary greatly. Some babies are born with a full head of hair, while others may have very little hair. The type of hair that develops after birth can also differ from the hair that grew during fetal development.
Hair Color
Hair color is determined by the amount and type of melanin present in the hair shaft. Melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, which are located at the base of the hair follicle. The amount of melanin produced can vary between individuals and can be influenced by genetics.
Gender
As mentioned earlier, gender can also play a role in hair growth and appearance. Male fetuses tend to have more hair than female fetuses, and male babies may also have thicker, coarser hair.
Ultrasound Imaging of Fetal Hair
Ultrasound imaging can be used to visualize fetal hair development. However, it is important to note that the resolution of ultrasound images may not be high enough to accurately determine the type or amount of hair present. Additionally, hair may not be visible on ultrasound images depending on the position of the fetus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fetal hair development is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors. Understanding the different types of hair that can develop in a fetus, as well as the factors that can influence hair growth and appearance, can provide valuable insight into fetal development.
Identifying Potential Problems Through Ultrasound

Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs, tissues, and structures. Ultrasound is commonly used during pregnancy to monitor the growth and development of the fetus, as well as to check for any potential problems. Ultrasound can also be used to examine other parts of the body, including the hair.
During an ultrasound, the doctor will use a small handheld device called a transducer to send sound waves through the body. The sound waves bounce off the hair and other structures in the body, creating an image that can be seen on a computer screen.
One potential problem that can be identified through ultrasound is cleft lip. Cleft lip is a birth defect in which the lip does not form properly, resulting in a split or gap in the upper lip. Ultrasound can be used to detect cleft lip before birth, allowing doctors to plan for treatment after the baby is born.
Ultrasound can also be used to detect other hair-related problems, such as hair loss or thinning. However, it is important to note that ultrasound is not always the best method for diagnosing these issues, and other tests may be necessary.
It is important to note that not all insurance plans cover ultrasound, and the cost of the procedure can vary depending on the provider. Patients should check with their insurance provider to determine coverage and out-of-pocket costs.
Overall, ultrasound is a useful tool for identifying potential problems with the hair and other structures in the body. However, it is important to work with a qualified doctor to interpret the results and determine the best course of action.
Ultrasound and Other Body Parts
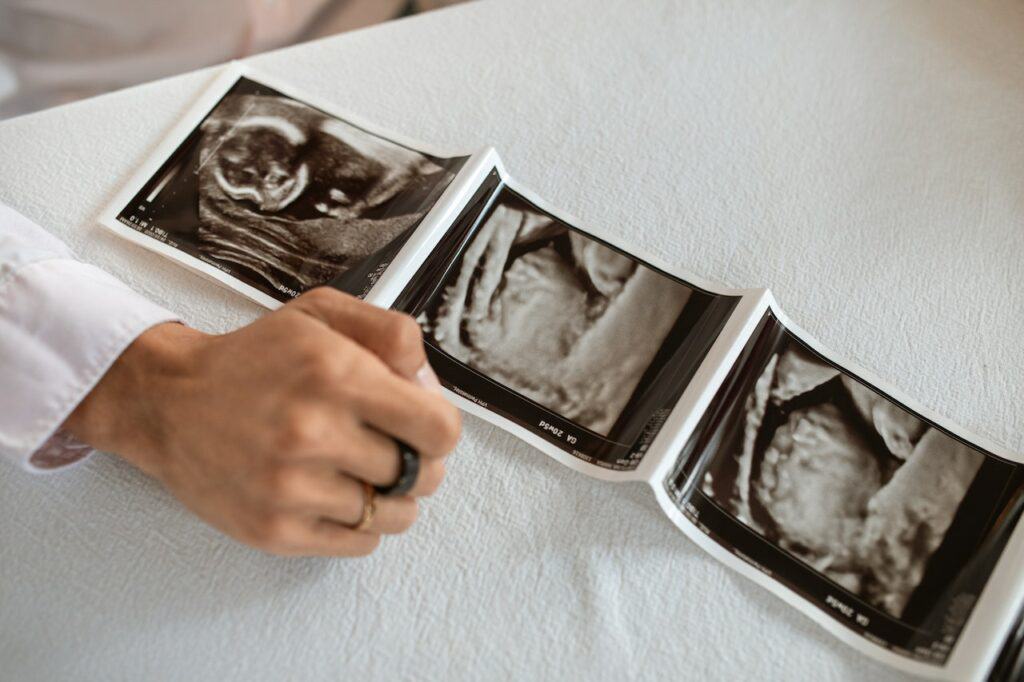
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal body parts. It is commonly used to examine organs, tissues, bones, and other structures in the body. However, ultrasound is not effective in imaging gas-filled structures, such as the lungs or bowel.
Ultrasound can be used to examine various organs in the body, such as the liver, kidneys, and spleen. The images produced by ultrasound can provide information about the size, shape, and texture of these organs, as well as the presence of any abnormalities, such as tumors or cysts.
In addition to organs, ultrasound can also be used to examine bones and soft tissues. Ultrasound can be used to detect fractures, joint injuries, and soft tissue injuries, such as muscle tears or ligament sprains. Ultrasound can also be used to guide injections into joints or soft tissues, such as cortisone shots or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections.
While ultrasound is not effective in imaging gas-filled structures, such as the lungs or bowel, it can be used to detect the presence of fluid in the lungs or around the heart. Ultrasound can also be used to evaluate the function of the heart, including the pumping action of the heart and the movement of blood through the heart and blood vessels.
In summary, ultrasound is a versatile diagnostic tool that can be used to examine a variety of body parts, including organs, bones, and soft tissues. While it is not effective in imaging gas-filled structures, such as the lungs or bowel, it can be used to detect fluid in the lungs or around the heart. Ultrasound is a safe and non-invasive procedure that can provide valuable diagnostic information to healthcare providers.
Special Considerations for Premature Babies
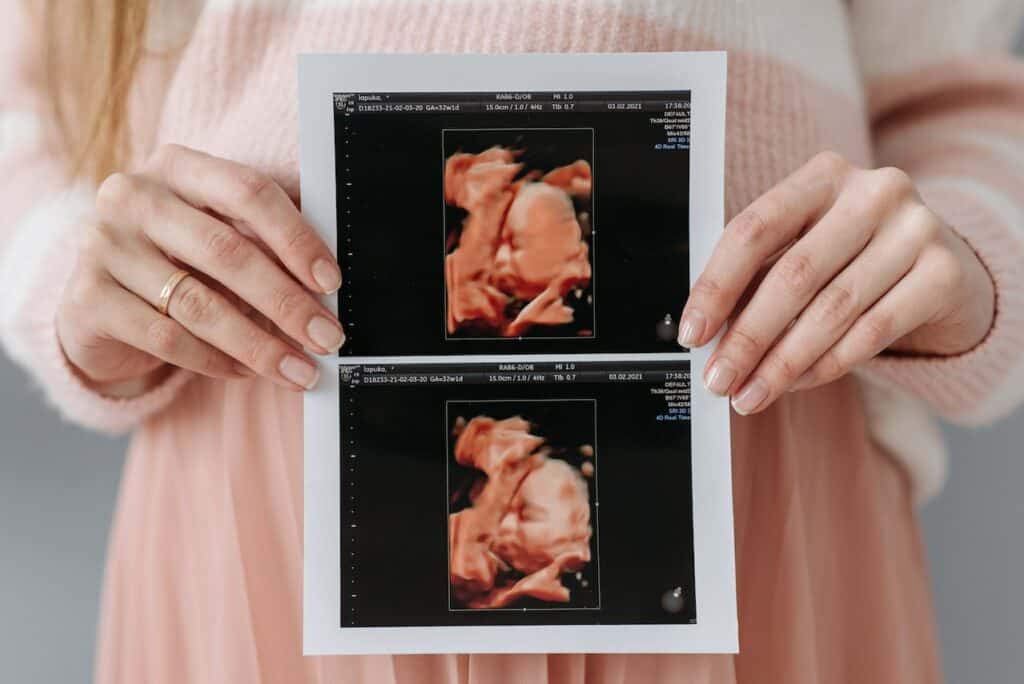
When it comes to ultrasounds and premature babies, there are a few special considerations that need to be taken into account. Premature babies may have less hair than full-term babies, and their hair may also be finer and sparser. This can make it more difficult to see hair on an ultrasound.
Additionally, premature babies may have a softer skull than full-term babies, which can make it more difficult to get a clear ultrasound image. In some cases, the ultrasound technician may need to use a special type of ultrasound probe or adjust the settings on the ultrasound machine to get a clearer image.
It’s important to note that the amount of hair on a premature baby’s head can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including their gestational age, overall health, and genetics. Some premature babies may have a full head of hair, while others may be completely bald.
Overall, it’s important to work with an experienced ultrasound technician who is familiar with working with premature babies to ensure that the images obtained are as clear and accurate as possible. By taking these special considerations into account, it is possible to get a clear image of a premature baby’s hair on an ultrasound.
Related post: Can a Doctor Determine Previous Pregnancy
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you see baby hair on an ultrasound?
Yes, it is possible to see baby hair on an ultrasound. However, it depends on the stage of pregnancy and the position of the baby.
What is the earliest stage of pregnancy you can see hair on an ultrasound?
Hair on a baby’s head begins to grow around the 14th week of pregnancy. It is possible to see hair on an ultrasound around this time, but it may not be visible in all cases.
Is it possible to tell the color of a baby’s hair on an ultrasound?
No, it is not possible to determine the color of a baby’s hair on an ultrasound. Hair color is determined by genetics and can only be observed after birth.
How can you determine if a baby has hair on a 3D ultrasound?
A 3D ultrasound provides a more detailed view of the baby, making it easier to see if the baby has hair. However, it still depends on the position of the baby and the quality of the ultrasound.
At what stage of pregnancy is it most common to see hair on an ultrasound?
Hair on a baby’s head is most commonly visible on an ultrasound during the third trimester of pregnancy. However, it may be visible earlier or later depending on the individual pregnancy.
What factors can affect the visibility of hair on an ultrasound?
The position of the baby, the quality of the ultrasound equipment, and the amount of amniotic fluid can all affect the visibility of hair on an ultrasound. Additionally, the amount and thickness of the hair can also impact its visibility.

Iesha is a loving mother of 2 beautiful children. She’s an active parent who enjoys indoor and outdoor adventures with her family. Her mission is to share practical and realistic parenting advice to help the parenting community becoming stronger.
